
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomManaging risk is one of the most important skills in trading and investing. Beyond simple diversification, portfolio theory introduces advanced concepts like the zero beta portfolio, a strategy designed to eliminate exposure to market risk.
In this guide, we explain what a zero beta portfolio is, how it is derived from the beta formula, its importance in modern finance, and provide a practical example.
What Is a Zero Beta Portfolio?
A zero beta portfolio is a theoretical portfolio whose beta equals zero, meaning it has no correlation with market movements.
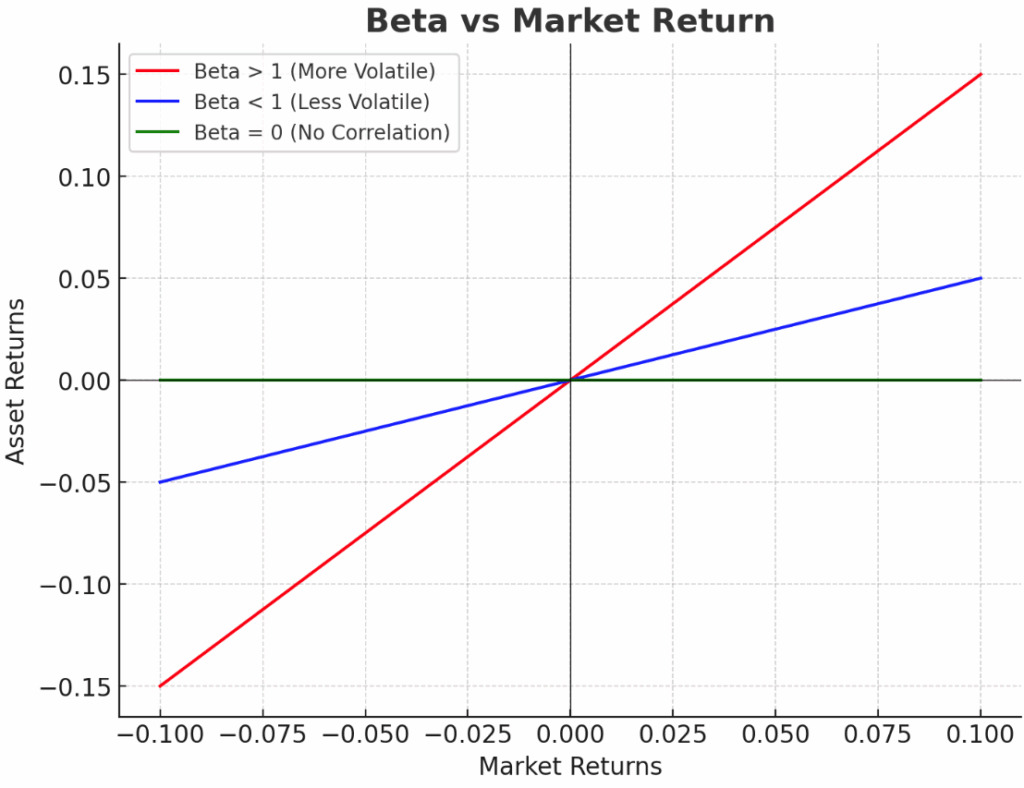
- Beta measures how sensitive an investment is to market movements.
- A beta of 1 means the portfolio moves in line with the market.
- A beta greater than 1 means higher volatility than the market.
- A beta of 0 means no correlation with the market index, so the portfolio eliminates systematic (market) risk.
In the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), the zero beta portfolio is used as an alternative to the risk-free asset, particularly in environments where a true risk-free instrument (such as U.S. Treasury bills) is unavailable or unreliable.
A zero-beta portfolio is not risk-free. It still carries idiosyncratic (asset-specific) risk, even though it avoids market-wide volatility.
Understanding the Beta Formula
The beta formula measures how sensitive an asset or portfolio is to movements in the overall market. It is defined as:
Beta = Covariance (Asset Return, Market Return) ÷ Variance (Market Return)
- Covariance (Ri, Rm): This shows how the asset’s return moves relative to the market’s return. If both tend to rise and fall together, the covariance is positive. If they move in opposite directions, it is negative.
- Variance (Rm): This measures how volatile the market itself is. A larger variance means the market has bigger swings.
By dividing covariance by variance, beta standardises the relationship between the asset and the market:
- A beta of 1 means the asset moves in line with the market.
- A beta greater than 1 means the asset is more volatile than the market.
- A beta less than 1 but greater than 0 means the asset is less volatile than the market.
- A negative beta means the asset moves opposite the market (rare in practice).
- A beta of 0 means no correlation with market movements.
Beta is a cornerstone of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), helping traders and investors assess systematic risk and expected returns.
Zero Beta Portfolio Formula
The beta of a portfolio is the weighted sum of the betas of its individual assets. A zero beta portfolio is achieved when this weighted sum equals zero. In other words, you adjust the portfolio weights so that the positive and negative betas cancel each other out.
Portfolio Beta = (Weight of Asset 1 × Beta of Asset 1) + (Weight of Asset 2 × Beta of Asset 2) + … + (Weight of Asset n × Beta of Asset n)
To construct a zero beta portfolio, investors set the portfolio beta equal to zero:
Zero Beta Portfolio Condition: Σ (Weight × Beta) = 0
Step-by-step breakdown:
- Assign weights: Decide the proportion of each asset in the portfolio.
- Multiply by beta: Multiply each asset’s beta by its assigned weight.
- Add them up: Sum all the weighted betas.
- Adjust weights until the sum equals zero.
This ensures the portfolio has no correlation with the market index.
In CAPM, the zero beta portfolio can replace the risk-free asset if one does not exist. It shows that investors can eliminate systematic (market) risk, though idiosyncratic risk remains. It is a theoretical construct, valuable in finance education and modelling, even though true negative-beta assets are rare.
Zero Beta Portfolio Example
To understand how a zero beta portfolio works in practice, let’s walk through an example step by step.
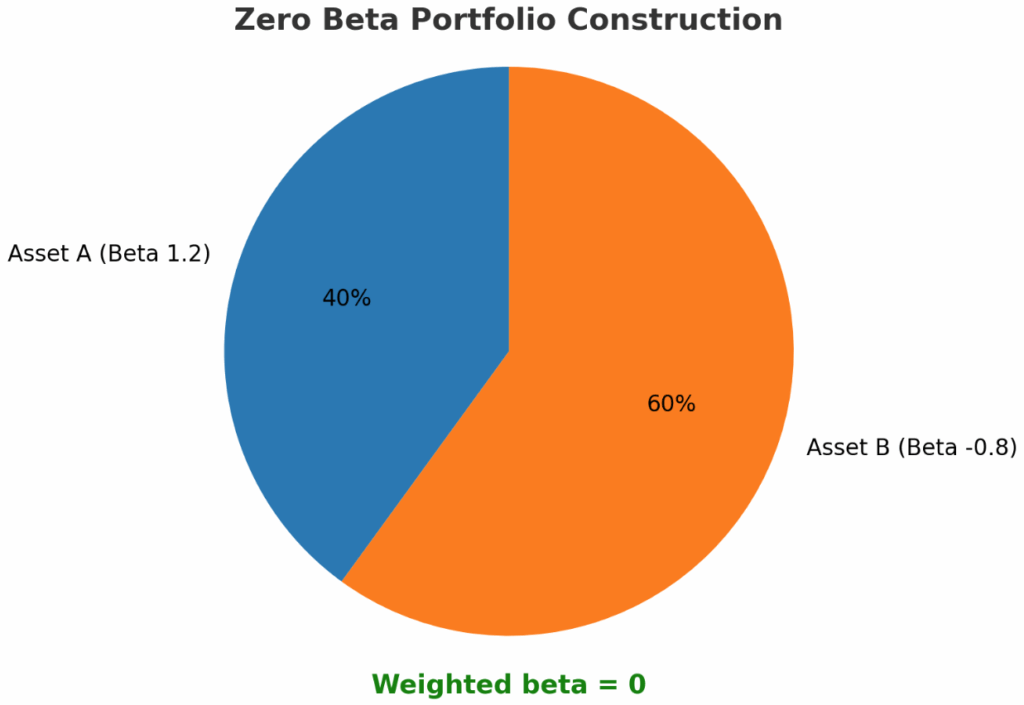
Define the assets, suppose we have two assets with different betas:
- Asset A: Beta = 1.2 (moves more than the market, higher volatility)
- Asset B: Beta = –0.8 (moves opposite to the market, negative correlation)
Set the goal
We want the portfolio beta (βp) = 0, meaning the portfolio has no correlation with the market.
Apply the formula
Portfolio Beta = (Weight of Asset A × Beta of Asset A) + (Weight of Asset B × Beta of Asset B)
Let’s assign weights:
- Weight of Asset A = 40% (0.4)
- Weight of Asset B = 60% (0.6)
Calculation:
βp = (0.4 × 1.2) + (0.6 × –0.8) = 0.48 – 0.48 = 0
Result: This portfolio has a beta of zero.
The portfolio is now uncorrelated with the market index. If the market rises or falls, the portfolio’s expected return should not be affected by systematic risk. However, the portfolio is not risk-free. It still faces idiosyncratic risk and sector risk.
While the example looks simple, constructing a true zero beta portfolio is difficult in practice because assets with stable negative betas are rare. Market correlations can shift over time, meaning today’s zero beta portfolio may not remain zero tomorrow. Most investors prefer risk-free assets (like government bonds) as a safer alternative.
Features of a Zero-Beta Portfolio
The importance of a zero beta portfolio lies in its role in financial theory:
- Extends CAPM: Provides an alternative to the risk-free asset when none exists.
- Capital Market Line: Demonstrates that equilibrium can exist without a risk-free security.
- Educational tool: Clarifies the difference between systematic vs unsystematic risk.
- Emerging markets relevance: Useful in markets where government bonds may not act as stable risk-free assets.
Zero Beta Portfolio vs. Risk-Free Asset
A zero beta portfolio and a risk-free asset both aim to reduce market risk, but they are not the same. A risk-free asset is completely safe, while a zero beta portfolio is only free from market risk, not all risks.
- Zero Beta Portfolio: A portfolio constructed so that its beta equals zero. It has no correlation with market returns and removes systematic (market) risk, but still carries idiosyncratic risk from the underlying assets.
- Risk-Free Asset: A security such as U.S. Treasury bills that is assumed to have no risk at all, neither systematic risk nor idiosyncratic risk.
| Feature | Zero Beta Portfolio | Risk-Free Asset |
| Correlation with Market | Zero (uncorrelated with index) | Zero |
| Systematic Risk | Eliminated | Eliminated |
| Idiosyncratic Risk | Still present | None |
| Example | Mix of stocks with positive & negative betas | U.S. Treasury bills, cash, govt bonds |
Conclusion
The zero beta portfolio is an important concept in modern portfolio theory and CAPM. While it is mainly a theoretical construct, it helps traders and investors understand how systematic risk can be eliminated through asset allocation. By balancing assets with positive and negative betas, a portfolio can achieve zero correlation with the market, although idiosyncratic risks will always remain.
At Ultima Markets, we believe that successful trading begins with education and a strong understanding of risk management. Our platform provides access to advanced tools, multi-asset markets, and educational resources designed to help traders make informed decisions. Whether you are learning about portfolio theory or applying strategies in real markets, Ultima Markets empowers you to trade with purpose and clarity.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












