Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: UK clients are kindly invited to visit https://www.ultima-markets.co.uk/. Ultima Markets UK expects to begin onboarding UK clients in accordance with FCA regulatory requirements in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United Kingdom
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Bear Put Spread: How to Use this Strategy
A Bear Put Spread is a powerful options strategy designed for traders who anticipate a moderate decline in the price of an underlying asset. Unlike more aggressive strategies that involve outright buying puts, the Bear Put Spread offers a way to limit risk while still profiting from a bearish outlook.
By combining the purchase of a higher-strike put with the sale of a lower-strike put, this strategy provides a defined risk-reward profile. In this guide, we’ll break down how the Bear Put Spread works, provide an example, and compare it to other similar strategies, helping you make more informed trading decisions.
What is a Bear Put Spread?
A Bear Put Spread is an options trading strategy where a trader buys a put option at a higher strike price and sells a put option at a lower strike price. This strategy is used when a trader expects a moderate decline in the price of an underlying asset. The goal is to profit from the price drop while limiting potential losses to the net premium paid for the options.
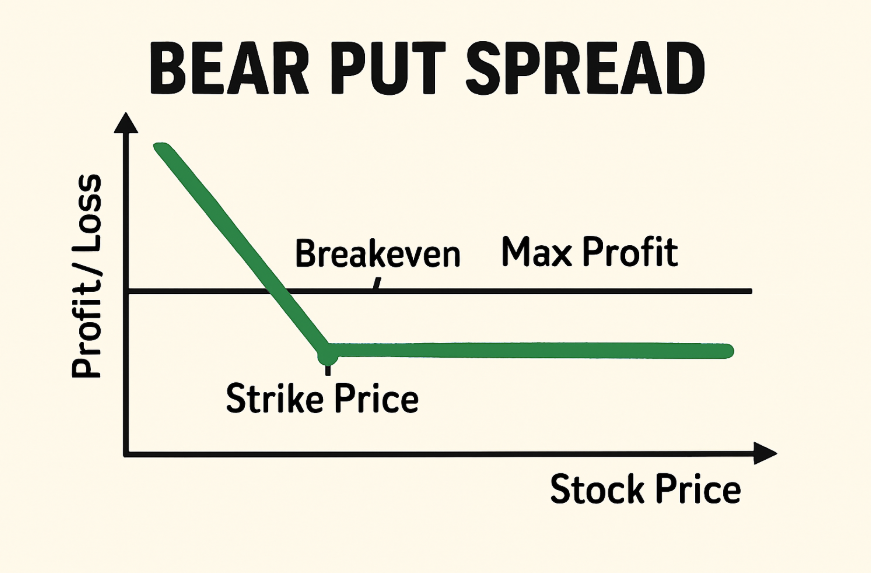
How Does A Bear Put Spread Work?
A Bear Put Spread works by combining two put options with different strike prices. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it functions:
- Buy a Put Option: The trader purchases a put option at a higher strike price. This gives the right to sell the asset at that price.
- Sell a Put Option: Simultaneously, the trader sells a put option at a lower strike price. This obligates the trader to buy the asset at the lower price if the option is exercised.
The premium received from selling the lower strike put helps offset the cost of buying the higher strike put, making the trade more cost-efficient and reducing overall risk.
Example of a Bear Put Spread
Here are two examples of a Bear Put Spread strategy:
Example 1: Stock XYZ
Scenario:
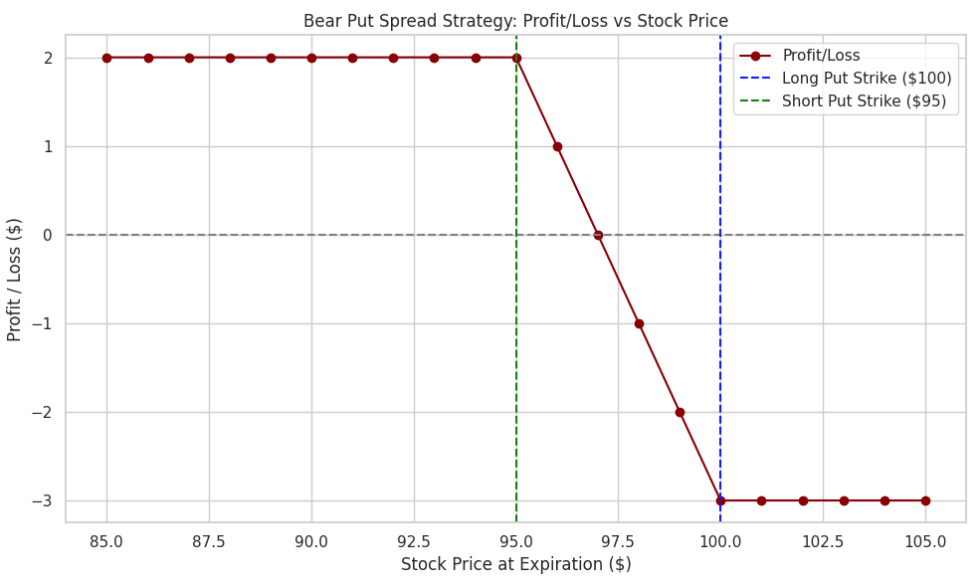
You believe that Stock XYZ, currently trading at $100, will experience a moderate decline over the next month. You decide to implement a Bear Put Spread to limit your risk while profiting from this expected decline.
- Buy a Put Option: Buy a put with a strike price of $100 for a premium of $5.
- Sell a Put Option: Sell a put with a strike price of $95 for a premium of $2.
Net Cost of the Trade:
The net premium paid is the difference between the two premiums:
$5 (buying the $100 put) – $2 (selling the $95 put) = $3.
Possible Outcomes:
- If Stock XYZ drops to $90 at expiration, the trader can sell at $95 (the strike price of the sold put) and buy it back at $90. This results in a profit of $5 (the difference between the strike prices) minus the $3 premium paid, for a net profit of $2.
- If Stock XYZ remains above $95, both options expire worthless, and the trader loses the $3 premium paid.
Example 2: Apple Inc. (AAPL)
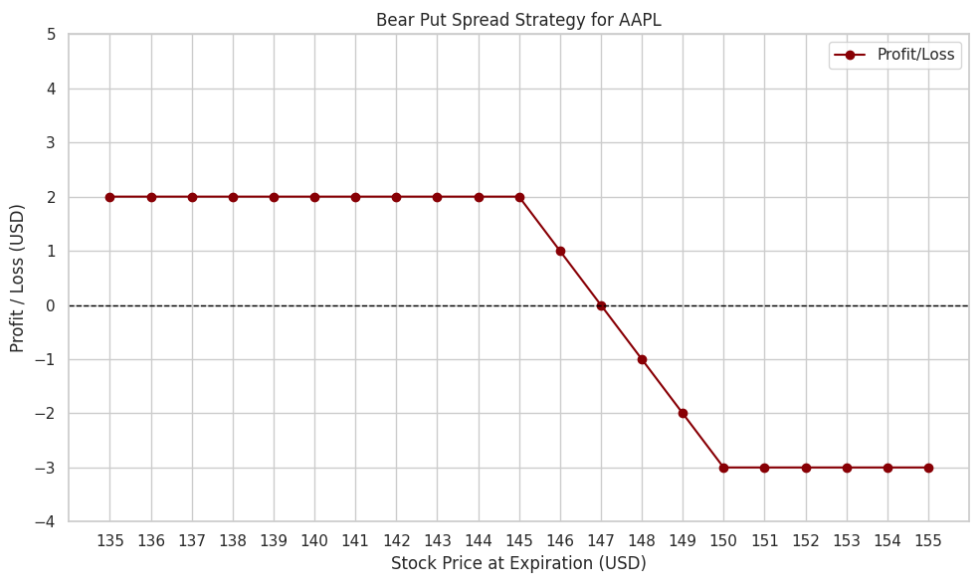
Scenario:
You believe that Apple Inc. (AAPL), which is currently trading at $150, will decline slightly due to market conditions in the upcoming weeks. You implement a Bear Put Spread to limit potential losses.
- Buy a Put Option: Buy a put with a strike price of $150 for a premium of $7.
- Sell a Put Option: Sell a put with a strike price of $145 for a premium of $4.
Net Cost of the Trade:
The net premium paid is the difference between the premiums:
$7 (buying the $150 put) – $4 (selling the $145 put) = $3.
Possible Outcomes:
- If Apple’s stock price falls to $140 by expiration, the trader can sell at $145 (the strike price of the sold put) and buy at $140, making a $5 profit (the difference between the strike prices), minus the $3 premium paid, for a net profit of $2.
- If the price stays above $145, the options expire worthless, and the trader loses the $3 premium paid.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bear Put Spread
The Bear Put Spread strategy offers traders a way to profit from a moderate decline in an asset’s price while controlling potential risks. Like any trading strategy, it comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. In this section, we’ll explore the key benefits of using a Bear Put Spread, such as limited risk and cost efficiency, as well as its drawbacks, including capped profit potential and reliance on price movement. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for making informed trading decisions and utilizing this strategy effectively.
Advantages:
- Limited Risk: The maximum loss is the net premium paid for the trade. This makes it a more conservative strategy compared to outright buying puts.
- Cost Efficiency: The strategy reduces the cost of buying a long put by selling another put with a lower strike price, making it less expensive to implement.
- Profit from Moderate Decline: The Bear Put Spread allows traders to profit from moderate declines in the price of the underlying asset, which can be an advantage in volatile markets.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Profit Potential: The maximum profit is capped by the difference between the two strike prices, minus the premium paid for the position.
- Requires Price Movement: For the strategy to be successful, the price of the underlying asset must decline. If the price does not fall enough, the trade may not be profitable.
- Misses Large Declines: If the underlying asset falls below the lower strike price, the trader will not benefit from the additional price decline beyond the maximum profit.
Bear Put Spread vs Bear Call Spread: Key Differences
Both Bear Put Spreads and Bear Call Spreads are options strategies designed for bearish market conditions, but they are structured differently:
- Bear Put Spread: Involves buying a higher-strike put and selling a lower-strike put. This strategy profits from moderate price declines in the underlying asset.
- Bear Call Spread: Involves selling a higher-strike call and buying a lower-strike call. This strategy profits when the price of the underlying asset stays below the higher strike price, often used in neutral to slightly bearish markets.
Key Differences:
- Risk: The Bear Put Spread has limited risk, with the maximum loss being the net premium paid. In contrast, the Bear Call Spread can expose traders to greater risk if the price of the underlying asset rises above the upper strike price.
- Profit Potential: The Bear Put Spread’s profit is capped by the price difference between the two strikes, whereas the Bear Call Spread’s maximum profit comes from the premium received from selling the call options.
Conclusion
The Bear Put Spread is a valuable options strategy for traders looking to profit from moderate declines in an asset’s price while keeping risk under control. With its defined risk and potential for cost-effective trades, it’s a solid choice for those navigating volatile markets.
At Ultima Markets, we provide traders with the tools and resources to implement strategies like the Bear Put Spread with ease. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, our platform’s comprehensive educational materials, advanced charting tools, and reliable execution help you execute your trades with confidence. Trade smarter, not harder, with Ultima Markets, your trusted partner in trading success.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












