Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomWhat Does O/C Mean in Trading?
O/C in trading stands for Over-Collateralization, a strategy where the value of collateral posted exceeds the value of the loan or financial exposure. It reduces risk for lenders and is commonly used in crypto lending, structured finance, and margin trading.
What Is Over-Collateralization?
Over-collateralization is a risk management strategy where a borrower provides collateral that exceeds the value of the loan. It protects lenders by ensuring they can recover their funds even if the collateral’s value falls due to market volatility.
In trading and structured finance, O/C is frequently used in:
- Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs)
- Stablecoins in DeFi (e.g., DAI, backed by crypto assets)
- Margin lending and repo agreements
This strategy acts as a buffer for investors and helps maintain system solvency in volatile markets.
In simple terms, over-collateralization means you give more value in assets than the amount you borrow. For example, if you borrow $1,000, you might need to provide $1,500 in collateral. This extra amount helps protect the lender in case the value of your collateral drops. It’s a common safety measure in both crypto and traditional finance.
What Is the Collateralization Ratio?
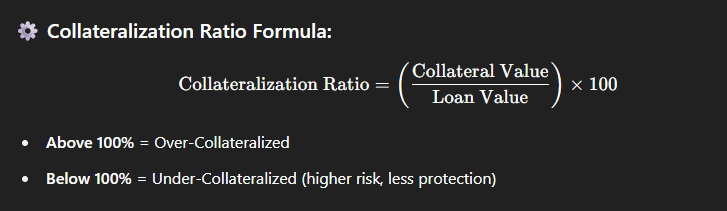
The Collateralization Ratio (CR) is the ratio of the value of the collateral to the value of the loan. It is calculated as:
Collateralization Ratio = (Collateral Value / Loan Value) × 100
- A CR above 100% means the loan is over-collateralized.
- A CR below 100% indicates under-collateralization and poses a higher risk to lenders.
This ratio is crucial in automated trading systems, lending platforms, and structured products.
How Over-Collateralization (O/C) Works?
Over-Collateralization (O/C) works by requiring a borrower to lock up more assets than the amount they intend to borrow. This extra cushion acts as protection for the lender or protocol in case the collateral’s value drops due to market volatility.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Borrower Deposits Collateral
The borrower deposits an asset such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or bonds into a lending protocol or financial institution. Example: $15,000 worth of ETH.
Loan Issued Based on Collateral Ratio
The borrower is granted a loan that is less than the value of the collateral, often based on a preset Collateralization Ratio (CR). If the CR is 150%, the borrower can receive a $10,000 loan against $15,000 in collateral.
Real-Time Monitoring (in DeFi and some TradFi systems)
Many platforms automatically monitor collateral value. If the value of the collateral drops and the CR falls below a liquidation threshold, the platform can begin partial liquidation to protect itself.
Liquidation Triggers
In DeFi, smart contracts will sell off a portion or all of the collateral to cover the outstanding loan.
Example: If ETH price drops by 30%, your CR may fall below 130%, triggering liquidation.
Collateral Returned if Repaid
Once the borrower repays the loan and interest, the entire collateral is returned, minus any penalties or fees.
For traders, over-collateralization ensures system solvency, helps secure better borrowing rates, and lowers counterparty risk. However, it also means capital inefficiency, as more assets are locked up than the actual loan amount, limiting liquidity.
Benefits of Over-Collateralization
From a trader’s perspective, the key benefits of over-collateralization include:
Lower Counterparty Risk
By requiring excess collateral, the lender minimizes exposure to default, particularly in volatile markets.
Higher Creditworthiness
Over-collateralized borrowers are often seen as more trustworthy, enabling them to access lower interest rates.
Resilience in Volatile Markets
In the DeFi ecosystem, over-collateralization is a foundational concept to keep stablecoins stable and lending pools solvent.
Automated Liquidation Safety Nets
DeFi smart contracts automatically trigger liquidations when the CR falls below a threshold, reducing systemic risk.
Over-Collateralization Example
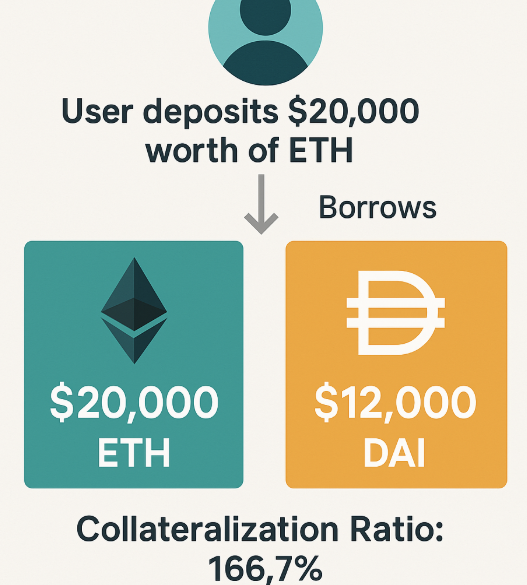
Here’s a real-world DeFi example:
- A user deposits $20,000 worth of ETH into a decentralized lending platform.
- They borrow $12,000 worth of DAI, a stablecoin.
- The resulting Collateralization Ratio is 166.7%.
If ETH’s value drops significantly, and the CR falls below the liquidation threshold (e.g., 130%), the system will automatically liquidate part of the ETH to maintain solvency.
Use of O/C in Traditional Trading Systems
Over-collateralization is not limited to crypto. It is used extensively in:
Asset-Backed Securities (ABS)
Where excess collateral enhances credit ratings.
Repo Markets
Traders use over-collateralized positions to borrow cash by selling securities with an agreement to repurchase.
Securitized Lending Structures
Banks structure deals with O/C to protect bondholders and attract institutional investors.
Conclusion
Over-Collateralization (O/C) is a vital tool in both traditional and decentralized markets to minimize risk, maintain system stability, and build trust between borrowers and lenders. Whether you’re trading crypto assets, managing leveraged positions, or navigating structured finance, understanding how O/C works gives you a competitive edge.
At Ultima Markets, we prioritize risk-managed trading environments that align with the latest financial innovations. Our platform supports institutional-grade security, smart risk control tools, and education to help traders stay ahead, especially in volatile markets where strategies like over-collateralization make all the difference.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.