Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomThe Australian Dollar (AUD) has been facing significant weakness in recent years, leading to concerns among traders and investors. Several key factors contribute to this decline, including shifts in global economic conditions, domestic monetary policy, and commodity price fluctuations. In particular, lower interest rates set by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA), economic slowdown, and ongoing trade tensions have placed considerable pressure on the value of the AUD.
Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the current forex landscape and anticipate future movements in the Australian Dollar.

Why Is the Australian Dollar So Weak (Key Reasons)
The Australian Dollar’s recent decline can be attributed to a combination of domestic and global factors. Understanding these key reasons is essential for traders and investors who are looking to grasp the broader economic forces at play. In this section, we’ll explore the primary drivers behind the AUD’s weakness and how they continue to shape its performance in the global market.
Interest Rate Differentials
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) has been cutting interest rates in 2025, with the current cash rate at 3.60%. This rate is relatively lower than the Federal Reserve’s rate of 5.25%, narrowing the interest rate differential between the two currencies. When Australian interest rates are lower than those in other countries, foreign investors find it less attractive to invest in AUD-denominated assets, leading to a weaker AUD.
Economic Slowdown
Australia’s economic growth has been slower than expected, with GDP growth projections for 2025 revised down to 1.7%. The RBA’s downgraded forecasts, along with low productivity growth and rising unemployment (which is expected to reach 4.3% in 2025), are fueling concerns about the future performance of the economy. This outlook contributes to investor caution regarding the Australian Dollar.
Commodity Price Volatility
Australia is a major exporter of commodities, including iron ore, coal, and natural gas. Fluctuations in the global prices of these commodities directly impact the value of the AUD. In 2025, a slowdown in China’s economy, a major trading partner, has reduced demand for Australian commodities, leading to lower export earnings and further weakening the AUD.
Global Trade Relations
Trade relations, especially with China, have been volatile in recent years. As a commodity-exporting nation, Australia is sensitive to global trade tensions. Any slowdown in global trade, or disruptions in relations with key trading partners, such as China, contributes to AUD weakness.
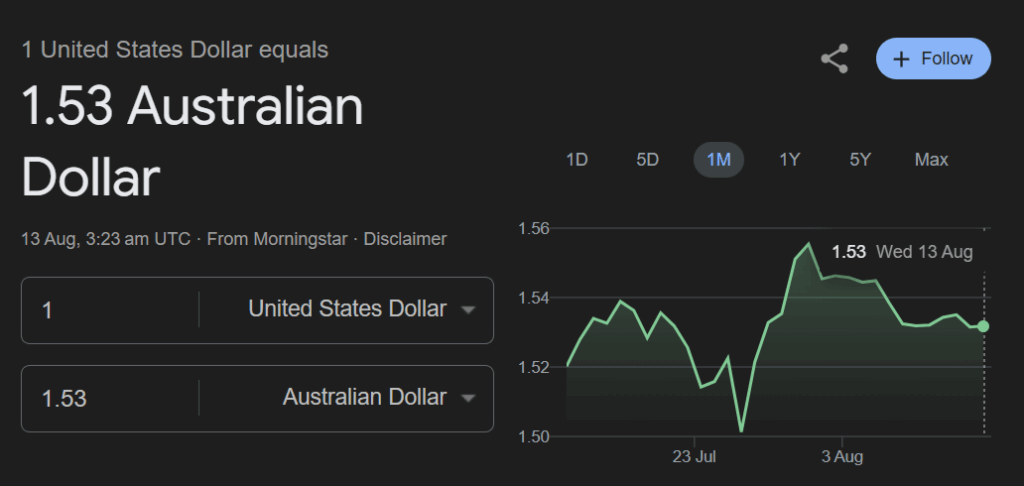
How the Australian Dollar to USD Exchange Rate is Impacted
The AUD/USD exchange rate is significantly influenced by the economic policies and conditions in both Australia and the United States. Here’s how:
US Dollar Strength
The US Dollar remains strong due to aggressive interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve, which has set its rates at 5.25% in 2025. This rate is substantially higher than Australia’s, attracting capital into USD assets and pushing the AUD/USD exchange rate lower. The stronger USD also reflects global investor preferences for safe-haven currencies amid geopolitical uncertainties and market volatility.
Economic Indicators
Both the RBA’s and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policies play crucial roles in the exchange rate. While the Fed’s stance has supported the USD, the RBA’s cautionary approach, lowering rates to stimulate economic growth has pressured the AUD. Furthermore, inflation, employment data, and GDP growth in both countries influence the exchange rate, with the current downward trend in Australia’s growth further weakening the AUD.
Popular Currency Pairs
The Australian Dollar is involved in many currency pairs, with AUD/USD being the most significant. Other popular currency pairs that involve the AUD include AUD/EUR, AUD/GBP, and AUD/JPY. The performance of these pairs is driven by:
AUD/USD
The most traded pair involving the Australian Dollar, the AUD/USD is directly affected by the interest rate differential, economic data from both countries, and global sentiment toward riskier assets. A weaker AUD means the pair will be priced lower against the USD.
AUD/EUR
This currency pair shows how the Australian Dollar compares to the Euro, and its movement is influenced by economic conditions in the Eurozone and broader global trends. A global risk-off sentiment tends to weaken the AUD against the Euro.
AUD/GBP
The AUD/GBP pair moves based on the relative strength of the UK economy versus Australia’s. With ongoing Brexit-related uncertainty and economic slowdowns in both regions, this pair can show heightened volatility.
AUD/JPY
The AUD/JPY pair often moves in line with global risk sentiment. When markets are risk-on, the AUD strengthens against the Yen. Conversely, in risk-off environments, the AUD tends to weaken relative to the Yen.
Future Outlook for the Australian Dollar
RBA Policy and Economic Outlook
The future of the Australian Dollar largely depends on the actions of the Reserve Bank of Australia. If the RBA continues its policy of rate cuts, the AUD may remain weak in the short-to-medium term. However, any economic recovery or stronger-than-expected GDP growth could provide support for the AUD.
Commodity Prices and Global Economic Conditions
A rebound in global commodity prices, particularly iron ore and coal, could help stabilize or even strengthen the Australian Dollar. Additionally, improving global trade relations and economic conditions could lead to more favorable prospects for the AUD.
Global Risk Sentiment
Risk sentiment plays a large role in currency markets. In a risk-on environment, the AUD tends to strengthen, but in times of global uncertainty, such as during geopolitical tensions or financial crises, the AUD usually weakens as investors flock to safe-haven currencies like the USD and JPY.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Australian Dollar’s weakness is driven by several interconnected factors, including interest rate differentials, economic performance, commodity price fluctuations, and global trade tensions. As these elements continue to evolve, it’s essential for traders to stay informed and adapt their strategies accordingly.
At Ultima Markets, we provide real-time market insights, advanced trading tools, and educational resources to help you navigate currency fluctuations and make smarter trading decisions. Stay ahead of the curve and trade with purpose, join Ultima Markets today.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












