Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this websiteWhy Is Pound Stronger Than Dollar?
The pound is stronger than the dollar because of long-standing differences in currency valuation, monetary policy, and market expectations. The Bank of England often maintains tighter interest rate policies, and investor confidence in UK assets can drive demand for the pound. A strong pound reflects relative economic performance and interest rate advantages over the dollar.
But before that, let’s understand what makes a currency strong.
What Makes A Currency Strong
A strong currency is one that maintains high purchasing power and performs well against other currencies in the foreign exchange market. It is typically backed by a stable economy, low inflation, and relatively high interest rates set by the central bank. Strong currencies attract foreign investment, are less volatile, and signal global confidence in the issuing country’s economic and political stability. Central bank policy, trade balances, and overall market demand play key roles in determining a currency’s strength.
A strong currency is one that performs well against its peers due to:
- Higher interest rates relative to competitors
- Low inflation
- Positive economic sentiment
- Capital inflows and investment demand
- Strong fiscal and trade positions
In forex, strength is always relative. Even if both economies are slowing, the one performing less poorly may have the stronger currency.
Why Pound Stronger Than Dollar? Key Reasons
To understand why the pound is stronger than the dollar, we need to look at the differences between the UK and US economies, especially in terms of interest rates, inflation, and central bank policy.
Interest Rate Expectations
As of July, the Bank of England’s base rate stands at 4.25%, while the US Federal Reserve rate is slightly higher at 5.00%. On paper, this might suggest the dollar should be stronger. However, forex markets are forward-looking. Traders expect the Fed to start cutting rates sooner due to cooling US inflation and slowing consumer demand. In contrast, the Bank of England is expected to hold rates higher for longer, due to persistent inflation pressures in the UK.
It’s not just about which central bank has higher rates now, but which one is expected to ease policy first. This outlook favors the pound.
Economic Outlook: UK vs US
The UK economy has shown signs of slowing. GDP contracted by –0.3% in April and –0.1% in May, and unemployment rose to 4.7%, the highest since 2021. Still, real wages are growing modestly, and inflation remains elevated at 3.6%, giving the Bank of England reason to stay cautious on rate cuts.
Meanwhile, in the United States, inflation has cooled to 2.5%, which gives the Fed more room to lower rates. Job growth is slowing, and consumer confidence declined in July. On top of that, the US fiscal deficit continues to widen, raising long-term concerns about dollar stability.
While both economies face challenges, the pound has a relative advantage due to tighter policy expectations and stronger near-term demand for UK assets.

The History Behind the Pound’s Higher Nominal Value
The British pound is one of the oldest currencies still in use, tracing its roots back to the 8th century. For most of modern history, it has held a higher face value than the US dollar. However, this doesn’t mean the UK has a stronger economy than the US. It’s largely a reflection of how each currency has been managed over time.
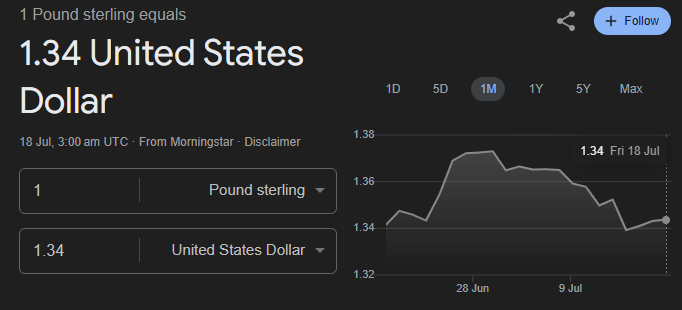
The pound’s higher nominal value (for example, £1 = $1.30 or more) is shaped by historical valuation methods, monetary policy differences, and inflation trends. The US dollar has undergone multiple inflationary cycles, especially during the 1970s stagflation and the aftermath of the 2008 global financial crisis. In contrast, the UK implemented more conservative monetary measures during similar periods, which helped preserve the pound’s relative value.
Another reason for the pound’s strength lies in its structural foundation. The British currency operates under a tighter money supply, lower currency circulation, and a more traditional banking framework. These factors have helped shield the pound from devaluation pressures that have impacted other major currencies over time.
Ultimately, while the pound is more valuable in nominal terms, it doesn’t necessarily reflect superior economic performance. It reflects a historically different approach to monetary stability.
What Does A Strong Pound Mean?
A strong pound means the British currency has a higher value compared to other currencies, especially major ones like the US dollar or euro. When the pound is strong, UK consumers benefit from cheaper imports, lower travel costs, and increased purchasing power abroad. However, it can make UK exports more expensive, potentially reducing demand for British goods overseas.
A strong pound often reflects positive market sentiment, higher interest rates, and economic stability in the United Kingdom. For forex traders, it signals upward momentum in GBP currency pairs like GBP/USD.

Pound vs Dollar Forecast: What Do Analysts Say?
Top financial institutions maintain a bullish outlook on the GBP/USD pair, supported by central bank divergence and a weakening US dollar. Here’s what the latest forecasts say:
JPMorgan
Forecast: GBP/USD to reach 1.32 by year-end
JPMorgan expects the pound to regain strength in the second half of the year, driven by a more cautious Bank of England and slower Fed easing. While short-term dips are possible, they project a recovery toward 1.32 by December.
ING
Forecast: GBP/USD heading toward 1.34 in 12 months
ING maintains a bullish outlook, forecasting a gradual climb to 1.34, assuming the Bank of England delays rate cuts while the US Federal Reserve begins easing. They cite relative monetary policy divergence as the key driver.
Goldman Sachs
Forecast: GBP/USD range of 1.33 to 1.35, possibly higher
Goldman Sachs remains positive on the pound, projecting the exchange rate to rise to 1.33–1.35 within the next 6–12 months. Some updated outlooks even suggest the potential for GBP/USD to hit 1.39, if UK inflation remains elevated and the Fed turns more dovish.
These forecasts highlight strong institutional confidence in the pound’s resilience, especially as markets price in earlier rate cuts from the Fed compared to the Bank of England.
Conclusion
The British pound’s higher nominal value compared to the US dollar is rooted in centuries of monetary history, inflation management, and conservative policy decisions, not necessarily stronger economic performance. For traders, this highlights the importance of looking beyond face value and focusing on macroeconomic trends, central bank outlooks, and real-time market sentiment.
At Ultima Markets, we help traders cut through the noise with expert analysis, real-time data, and transparent trading conditions so you can navigate major currency pairs like GBP/USD with confidence. Whether you’re trading short-term moves or long-term trends, understanding the true drivers behind currency strength is key to smarter decisions.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.