
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomWhat is Margin Trading?
Margin trading is a strategy that allows traders to borrow funds from a broker to open larger positions than their capital would normally permit. By using margin, traders can amplify both profits and losses, making it a high-risk, high-reward approach often used in forex, stocks, and crypto markets.
Unlike regular trading, where you use only your own money. Margin trading introduces borrowed capital into the equation, which is why it’s crucial to understand how margin trading works, its risks, and its role in a trading plan.

How Does Margin Trading Work?
In simple terms, margin trading involves borrowing money from your broker to increase the size of a trade. Traders must deposit a margin requirement, which acts as collateral. This margin is usually a percentage of the full trade size, depending on the instrument and broker’s leverage offering.
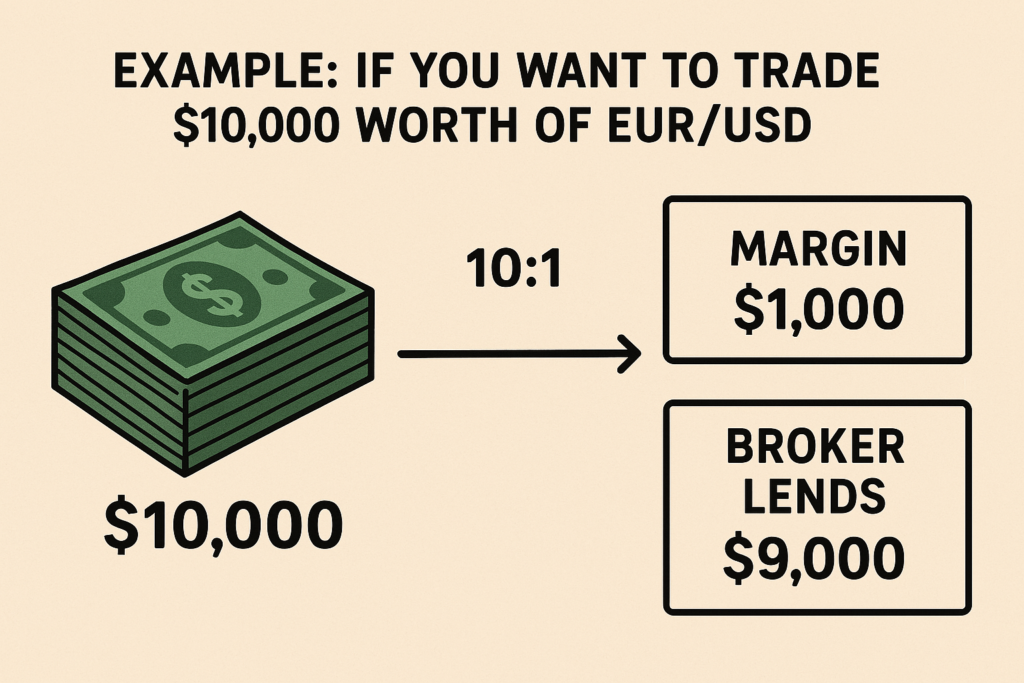
Example: If you want to trade $10,000 worth of EUR/USD and your broker offers 10:1 leverage, you’ll need only $1,000 in margin. The broker lends the remaining $9,000.
If the trade moves in your favor, profits are magnified. However, losses are also amplified. If your account drops below the maintenance margin, the broker may issue a margin call, forcing you to deposit more funds or close positions to cover the risk.
What’s the Difference Between Margin and Leverage?
Margin and leverage are closely related but not the same:
- Margin is the amount of money you need to open a leveraged trade.
- Leverage is the ratio that defines how much more exposure you can control with a given amount of capital.

For example, a 100:1 leverage ratio means you can control $100,000 in the market with just $1,000. In this context, the margin required is 1%.
Understanding this distinction is critical because it directly affects your risk per trade, margin requirements, and potential for losses.
Pros of Margin Trading
Margin trading offers several benefits for active and experienced traders:
Amplified Returns
With proper risk management, margin trading can significantly increase the return on investment by allowing larger trade sizes.
Diversification
Traders can open multiple positions across different markets without needing full capital for each trade.
Short-Selling Opportunities
Margin accounts typically allow both long and short positions, enabling traders to profit in rising or falling markets.
Cons of Margin Trading
Despite its benefits, margin trading carries considerable risks:
Magnified Losses
Just as profits can be amplified, so can losses. A small market move against your position can wipe out your capital.
Margin Calls and Liquidation
If your account value drops below the required margin level, your broker can issue a margin call or forcibly liquidate your positions.
High Psychological Pressure
The potential for rapid gains or losses can lead to emotional trading and poor decisions if not properly managed.
How to Trade on Margin Safely
Trading on margin requires discipline, a solid strategy, and strict risk control. Here’s how to trade on margin like a professional:
Understand Your Broker’s Margin Requirements
Each broker and asset class has different margin rates. Forex, for example, typically allows higher leverage than stocks.
Use Stop-Loss Orders
Protect your capital by setting stop-losses to exit trades if the market moves against you.
Monitor Margin Levels
Use your broker’s platform to track margin usage and avoid falling below the maintenance level.
Start Small
Beginners should avoid over-leveraging. Test your strategy on a demo account or use low leverage until confident.
Why Margin Trading Matters for Active Traders
Professional traders use margin not to gamble, but to maximize capital efficiency. For example, in forex trading, where currency movements are typically small (measured in pips), margin enables traders to scale trades to meaningful profit levels.
However, the best traders combine margin with risk management, only risking 1–2% of their capital per trade, regardless of the margin used. They also factor in volatility, news events, and position sizing to reduce exposure.
Is Margin Trading Right for You?
Margin trading is suitable for active traders who:
- Understand technical and fundamental analysis
- Can manage risk through stop-losses and position sizing
- Are disciplined and emotionally stable during market swings
It is not recommended for those who trade based on emotion or lack a clear trading plan. Always test your strategy and understand the full risk before using leverage.
Conclusion
Margin trading can be a powerful tool when used with proper education and risk control. It offers increased flexibility and profit potential but requires a deep understanding of how it works.
At Ultima Markets, we provide transparent margin policies, competitive leverage, and educational resources to help traders make informed decisions. Whether you’re trading forex, indices, or commodities, our platform equips you with real-time tools to manage your margin effectively.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












