Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomWhat is Compound Trading?
Compound trading is a long-term strategy where traders reinvest their profits to grow their capital exponentially. Unlike traditional trading, which may involve withdrawing profits or leaving them idle, compound trading uses the concept of compounding to generate more significant returns over time. By reinvesting profits consistently, traders can take advantage of the compound interest effect, which allows them to earn profits not just on the initial investment, but also on the gains made from previous trades.
This strategy works particularly well in financial markets such as forex, stocks, and commodities, where traders can take advantage of market movements over time. Compound trading requires patience, discipline, and a well-thought-out plan to maximize the benefits of compounding.
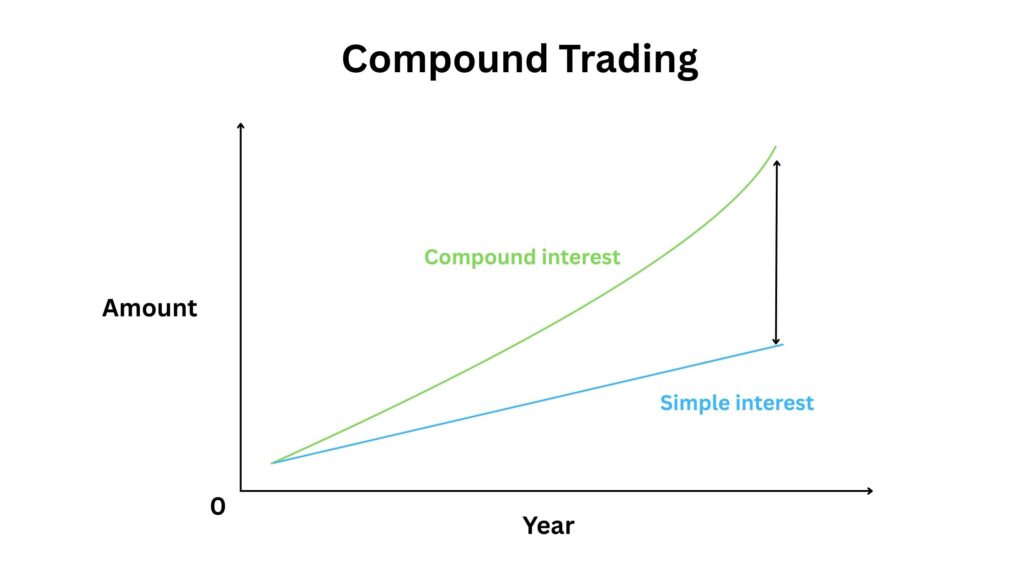
How Does Compound Trading Work?
In compound trading, the goal is to generate profits, then reinvest those profits to increase the size of future trades. Here’s how it works:
- Initial Investment: Start with a base amount of capital.
- Reinvestment of Profits: After each trade, reinvest your profits instead of withdrawing them.
- Exponential Growth: By continually increasing the size of your trades with reinvested profits, the returns grow exponentially over time, similar to how compound interest works in savings accounts.
By following this approach, traders can benefit from compounding over weeks, months, and years, allowing them to build significant wealth with a relatively small initial investment.
How to Start Compound Trading
Step 1: Educate Yourself on Trading Basics
Before engaging in compound trading, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals of the markets, including how different asset classes work and how to read charts and financial statements. Learn about technical analysis, risk management, and order types to help build a solid foundation.
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Trading Platform
Select a trading platform that offers features like automated trading tools, historical data analysis, and real-time market tracking. Ensure the platform is reliable, has low fees, and provides adequate educational resources for new traders.
Step 3: Develop a Long-Term Trading Plan
A well-thought-out plan is crucial for successful compound trading. Determine your trading goals, how much capital you’re willing to invest, and your reinvestment strategy. Decide whether you’ll compound profits daily, weekly, or monthly, and establish clear risk management rules to protect your capital.
Step 4: Start Small and Reinvest
Start with a small amount of capital to test your strategy, and as your profits grow, reinvest them into your trades. It’s essential to track your trades and ensure that your reinvestment strategy is working as intended.
Daily vs Monthly Compounding in Trading
Daily Compounding in Trading
Daily compounding refers to reinvesting profits at the end of each trading day. The main advantage of daily compounding is that it allows traders to maximize returns more quickly by taking full advantage of the compounding effect every single day. The more frequently profits are reinvested, the faster the growth.
However, daily compounding requires consistent monitoring of the markets and disciplined trading strategies. This approach works best for active traders who are comfortable with shorter trading time frames and have the time to manage their investments daily.
Monthly Compounding in Trading
Monthly compounding, on the other hand, involves reinvesting profits at the end of each month. While the growth rate is slightly slower compared to daily compounding, it can still offer significant long-term results. Many traders prefer monthly compounding because it’s less time-intensive and allows for more strategic planning.
For those who trade in longer time frames and focus on less frequent adjustments to their positions, monthly compounding can be an effective and low-maintenance strategy.
What is Compound Interest?
Compound interest is the process of earning interest on both the initial principal and the accumulated interest from previous periods. In trading, this concept is similar to reinvesting profits. As profits accumulate, they begin to generate returns on their own, leading to faster growth compared to simple interest, where interest is only earned on the principal.
In the context of trading, compound interest is applied to both capital gains and dividends or other types of earnings, amplifying returns over time. For instance, if you earn profits from a trade and reinvest those earnings into the next position, your profit will compound, generating additional profits.
Compound Trading in Bear vs Bull Markets
Compound Trading in Bull Markets
In a bull market, asset prices are rising, making it easier for traders to accumulate profits. Compound trading in a bull market can be very effective because each reinvested profit takes advantage of the prevailing upward trend. As the market rises, so do the potential returns, creating an ideal scenario for compound traders to see exponential growth in their portfolios.
To succeed in a bull market, compound traders need to maintain their positions and consistently reinvest profits as the market moves in their favor.
Compound Trading in Bear Markets
In a bear market, prices are falling, and the market sentiment is more pessimistic. However, compound trading can still be applied successfully by focusing on identifying short-term recovery opportunities or countertrend strategies. Risk management becomes even more important in a bear market, as traders may face losses before profiting.
Traders can compound their profits during bear markets by focusing on sectors that may be less impacted by the broader market downturn or by using risk-hedging techniques, such as stop-loss orders or short-selling.
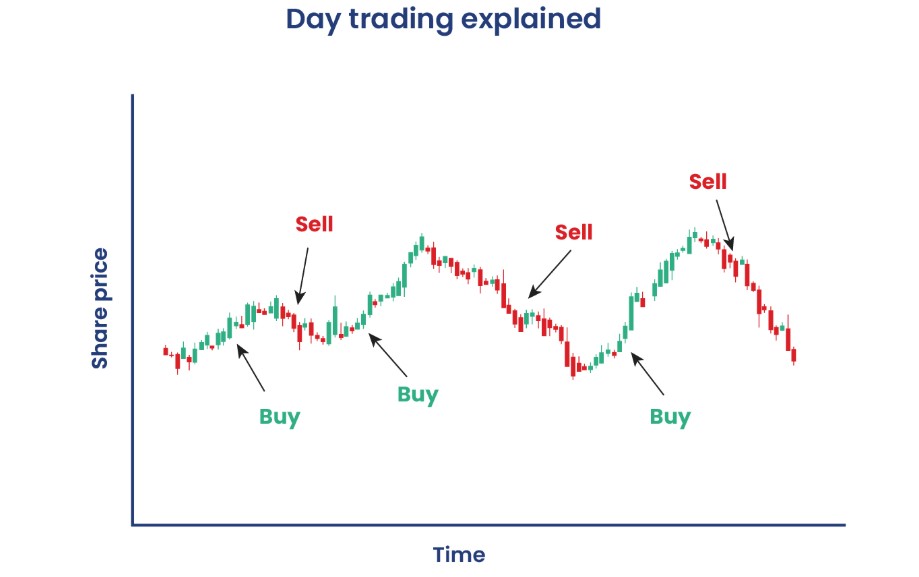
Compound Trading vs Day Trading
The key difference between compound trading and day trading is the time horizon. Compound trading is a long-term strategy that relies on patience and discipline to reinvest profits for exponential growth. Day trading, on the other hand, is more focused on short-term profits and fast decision-making.
While both strategies aim to generate profits, compound trading is better suited for those who want to take advantage of long-term market trends, while day trading is ideal for traders who are comfortable with high-frequency trades and short-term market movements.
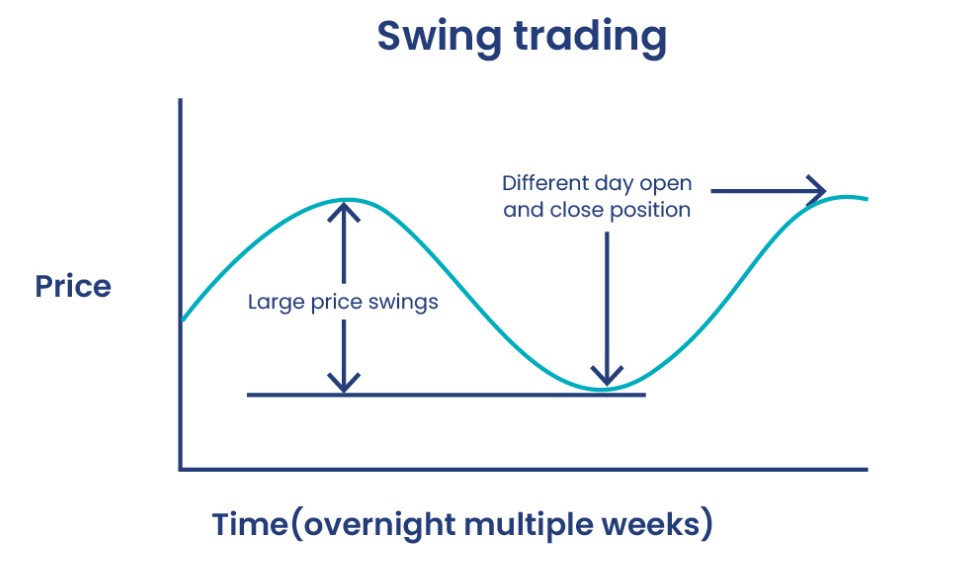
Compound Trading vs Swing Trading
The difference between compound trading and swing trading lies in the approach to profit generation. While swing traders focus on short- and medium-term trends, compound traders rely on long-term growth through reinvested profits. Compound trading focuses on capitalizing on the exponential growth of profits, while swing trading aims to capitalize on specific market swings without necessarily reinvesting profits.
Conclusion
Compound trading is a powerful strategy that offers traders the potential to build significant wealth over time by reinvesting profits for exponential growth. Whether in bull or bear markets, compound trading can work to your advantage when combined with the right knowledge, patience, and risk management. The key to success lies in choosing the right strategy, understanding market trends, and staying disciplined.
At Ultima Markets, we empower traders with the tools and resources needed to succeed, no matter your trading style. As a regulated CFD broker, we offer a secure and transparent trading environment where you can leverage compound trading strategies to enhance your portfolio. With our commitment to sustainability, supported by our UN Global Compact membership and FCA regulation, we ensure that you trade with purpose, backed by credibility and global standards.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.