Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this websiteWhat Currency Does Argentina Use?
Argentina uses the Argentine Peso, abbreviated as ARS, as its official currency. Managed by the Central Bank of Argentina (Banco Central de la República Argentina), the peso plays a central role in the nation’s economy but it’s also one of the most volatile currencies in Latin America.

What is the Currency Code for Argentina?
The currency code for Argentina is ARS. In forex markets, it typically appears in the format of USD/ARS, representing the exchange rate between the US Dollar (USD) and the Argentine Peso (ARS).
The peso is subdivided into 100 centavos, and coins and banknotes are issued in various denominations. Due to high inflation, Argentina regularly introduces new banknotes with higher face values.
USD/ARS Exchange Rate (as of July 2025)
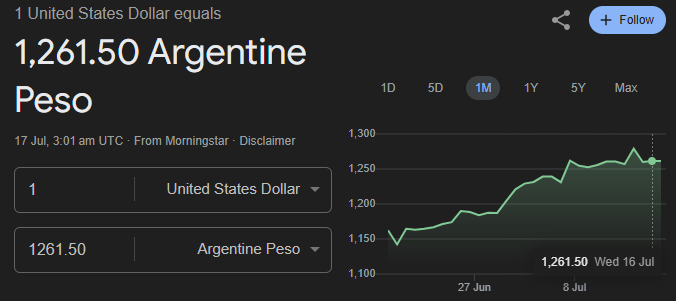
As of July 17, 2025, the exchange rate for USD/ARS stands at 1,261.50, meaning one US dollar equals 1,261.50 Argentine pesos. Over the past month, the peso has depreciated steadily against the dollar, rising from around 1,140 ARS to over 1,260 ARS per USD. This marks a depreciation of approximately 10.6% within just four weeks.
The upward slope in the chart reflects growing pressure on the peso, driven by monetary expansion, ongoing political uncertainty ahead of the October elections, and concerns over Argentina’s low foreign reserves. A sharp spike around mid-July signals intensified market reactions, possibly linked to fiscal policy news or investor sentiment shifts.
Overall, the trend shows continued weakness in the ARS, reinforcing bearish expectations in the USD/ARS forex pair and highlighting the currency’s vulnerability to domestic and external shocks. Traders should closely monitor central bank responses and FX band changes as the peso approaches the upper limit of Argentina’s managed float system.
Why Is Argentina’s Currency Falling?
The Argentine peso (ARS) continues to depreciate in 2025, though at a slower pace than in past years. Several macroeconomic and political forces are driving this trend:
High But Slowing Inflation
While Argentina once suffered triple-digit inflation, the government’s tight fiscal policy under President Javier Milei has reduced monthly inflation to 1.5%–1.6%, the lowest in five years. However, annual inflation still hovers around 40–47% YoY, one of the highest globally. This erodes the peso’s real value and keeps devaluation expectations alive among traders.
Currency Reform and Exchange Rate Band
In early 2025, Argentina scrapped strict FX controls and introduced a managed float system with an official USD/ARS trading band of 1,000 to 1,400. Despite the reforms, the peso trades near the top of that band, indicating persistent selling pressure and market skepticism toward full stabilization.
Low Reserves and Debt Obligations
Argentina’s central bank reserves remain critically low, around $9 billion. Despite securing a $20 billion IMF loan. Ongoing debt payments, limited foreign direct investment, and judicial rulings (like the YPF case) continue to weaken confidence in ARS-denominated assets.
Political and Fiscal Uncertainty
Though Milei’s government has made bold fiscal cuts, rising tensions with Congress and upcoming October 2025 elections are creating uncertainty. This political instability raises risk premiums on Argentine assets, increasing capital outflows and reducing peso demand.
- Trader Insights: ARS Outlook in 2025
FX Band Limits Speculation: The 1,000–1,400 band offers predictability, but traders see the peso pressing the upper ceiling, signaling limited trust in ARS appreciation. - Carry Trade Less Attractive: Despite high interest rates, peso-based instruments face volatility and liquidity concerns.
- Event-Driven Volatility: Markets react sharply to fiscal news, IMF reviews, and legislative votes especially those affecting pension reforms or reserve usage.

Argentina’s currency is still falling due to lingering inflation, low reserves, and investor caution amid political tension. Although capital controls have eased, the peso’s depreciation trend remains intact especially as elections approach and fiscal risks resurface. For traders, USD/ARS offers volatility-driven opportunities, but requires close monitoring of central bank actions, reserve levels, and policy developments.
USD/ARS Forex Pair: Key Trading Insights
The USD/ARS forex pair reflects the value of 1 US dollar in Argentine pesos. It is considered a non-major, exotic pair due to:
- Low liquidity compared to major pairs
- High volatility, often driven by government policies or IMF negotiations
- Frequent central bank interventions
As of mid-2025, USD/ARS trades at historically high levels, above 1,000 ARS per USD, with wide spreads due to capital controls and inflationary pressure.
- USD/ARS Trading Strategy Tips:
Monitor inflation and interest rates: The Central Bank’s benchmark rate (hovering around 70–90%) affects ARS pricing. - Watch IMF-related headlines: Agreements or delays in payments often spark sharp peso moves.
- Use caution with leverage: High volatility and low liquidity can lead to fast, large swings.
Popular Pairs for ARS in Forex Trading
Beyond USD/ARS, traders also watch these ARS currency pairs:
| Pairs | Description |
| EUR/ARS | Euro to Argentine Peso |
| GBP/ARS | British Pound to Argentine Peso |
| BRL/ARS | Brazilian Real to Argentine Peso |
| CLP/ARS | Chilean Peso to Argentine Peso |
These pairs are traded less frequently due to wider spreads, but can offer unique arbitrage or carry trade opportunities, especially during periods of Latin American currency volatility.
How Does Argentina’s Currency Impact Trade and Investment?
The depreciation of the Argentine peso (ARS) significantly influences the country’s trade dynamics, foreign investment flows, and overall capital market behavior. Here’s how:
Rising Import Costs
A weaker ARS makes foreign goods and services more expensive. Argentina heavily relies on imports for fuel, machinery, and pharmaceuticals. As the peso loses value, importers face higher costs, which:
- Shrinks consumer purchasing power
- Fuels inflation in USD-linked goods
- Forces companies to cut volume or pass on costs, impacting GDP
This worsens the trade deficit unless export earnings compensate.
Export Competitiveness Improves
On the flip side, a cheaper peso makes Argentine exports more attractive in global markets. This particularly benefits key sectors like:
- Agriculture (soybeans, corn, beef, wheat)
- Mining (lithium, copper, gold)
- Industrial goods (steel, auto parts)
Exporters earn in USD but pay local costs in ARS, improving margins. This helps stabilize Argentina’s trade balance, even amid volatile global demand.
Foreign Investment Remains Cautious
Despite Argentina’s rich natural resources and potential, exchange rate instability deters foreign capital. Key concerns include:
- Repatriation risk: Investors fear they’ll be paid in devalued pesos or blocked from converting returns into USD
- Currency mismatch: Projects financed in USD but generating ARS revenues face repayment risk
- Legal and fiscal unpredictability: Tax changes and debt rulings (e.g., YPF case) amplify FX-linked risk
This leads to underinvestment, especially in sectors requiring long-term USD funding like energy, infrastructure, and tech.
Dual Dollar Market Pressure
To hedge against peso losses, many Argentines convert savings into USD—either through legal dollar savings accounts or the parallel “blue dollar” market. This behavior:
- Increases demand for USD, pressuring reserves
- Widens the gap between official vs unofficial FX rates
- Reduces central bank control over monetary policy
It also triggers regulatory responses, such as temporary capital controls or currency band adjustments.
Conclusion
Understanding what currency Argentina uses, the ARS is more than just knowing its name. It’s about recognizing the economic fragility, volatility, and trading opportunities that come with it. Whether you’re monitoring USD/ARS, planning hedges, or navigating emerging markets, staying updated on Argentina’s inflation, policy decisions, and FX interventions is crucial.
For traders looking to access volatile pairs like USD/ARS, consider partnering with Ultima Markets, a regulated broker offering tight spreads, real-time economic data, and robust risk management tools helping you trade Latin American currencies with confidence.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.