
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomWhat Are Liquid Assets?
Liquid assets refer to assets that can be easily sold or exchanged for cash within a short time, typically without losing value. These include:
- Cash and cash equivalents (e.g. currency, bank balances)
- Money market instruments
- Publicly traded stocks and ETFs
- Government bonds with high demand
- Treasury bills and commercial paper
Traders and institutions prioritize liquid assets for fast execution, especially in volatile markets or during unexpected drawdowns.

Why Liquid Assets Matter?
For traders, liquidity is more than convenience. It is a risk management tool. Here’s why liquid assets matter:
- Quick Reaction to Market Volatility: Liquid assets enable traders to respond immediately to market news or price swings.
- Fulfilling Margin Requirements: During high volatility, brokers may issue margin calls. Holding liquid assets ensures traders can cover these calls without closing long-term positions.
- Execution Efficiency: Highly liquid markets reduce slippage and ensure orders are filled near intended prices.
Example: A trader holding U.S. Treasury bills can liquidate them faster and at fair market value compared to real estate or long-term private equity investments.
Example of Liquid Assets
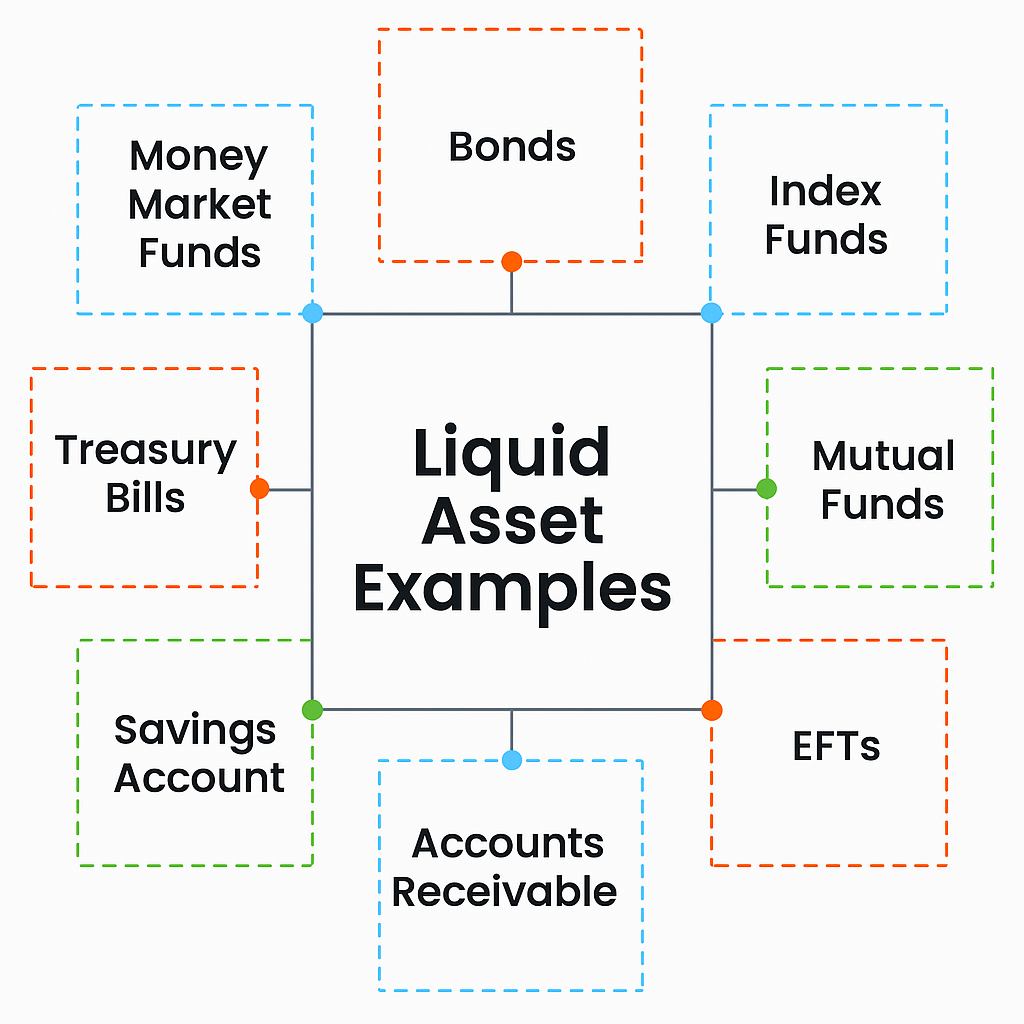
| Asset Type | Liquidity Level | Typical Use in Trading |
| Cash / Bank Deposits | High | Used for immediate transactions |
| Treasury Bills | High | Safe haven during risk-off sentiment |
| Money Market Funds | High | Temporary parking for idle capital |
| Publicly Traded Equities | Medium–High | Short-term speculation and hedging |
| ETFs | Medium–High | Diversified exposure with liquidity |
Liquid Assets vs Non-Liquid Assets
Understanding the difference between liquid and non-liquid assets helps traders manage portfolio risk more effectively.
| Aspect | Liquid Assets | Non-Liquid Assets |
| Convertibility | Quick (minutes to hours) | Slow (weeks to months) |
| Price Stability | Minimal impact on value when sold | High potential for discount or price distortion |
| Examples | Cash, stocks, T-bills | Real estate, art, private equity |
| Use in Trading | Capital deployment, risk buffer | Long-term holding, not ideal for quick trades |
Benefits of Liquidity Assets in Trading
Holding a percentage of your portfolio in liquidity assets provides:
- Better Risk Management: Easily accessible capital during drawdowns.
- Flexibility: Ability to enter or exit positions without delay.
- Improved Position Sizing: Avoids overleveraging by maintaining a liquidity buffer.
- Faster Capital Rotation: Enables quick reallocation into trending assets or sectors.
Pro Insight: Professional traders often allocate 10–30% of their portfolio to cash or equivalents during uncertain market conditions to maintain flexibility.
Risks of Liquidity Assets in Trading
While liquidity assets are vital, over-reliance can pose certain drawbacks:
- Lower Returns: Cash and equivalents offer minimal yield, especially during inflationary periods.
- Opportunity Cost: Capital parked in low-yielding assets could underperform compared to growth investments.
- Market Mispricing in Crisis: Even normally liquid assets (like stocks) may face temporary illiquidity during financial panics.
How to Manage Liquidity in Your Trading Portfolio
- Set Liquidity Targets: Allocate a fixed percentage of your portfolio to liquid assets.
- Diversify Within Liquid Instruments: Use a mix of cash, T-bills, and ETFs for strategic flexibility.
- Monitor Market Liquidity Conditions: Use tools like bid-ask spread, volume, and average daily turnover to assess asset liquidity.
- Plan for Contingencies: Always keep sufficient liquid assets to handle unexpected expenses or opportunities.
Conclusion
Liquidity assets are not just about preserving capital, they’re about staying ready. Whether you’re facing margin calls, unexpected volatility, or new trade opportunities, having access to liquid assets can mean the difference between reacting and missing out.
At Ultima Markets, we emphasize smart capital allocation. Our trading platforms are designed to support your liquidity needs from ultra-fast execution to access to highly liquid markets like forex, indices, and commodities. Whether you’re a short-term trader or managing long-term strategies, integrating liquidity assets into your portfolio is key to resilience and performance.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












