
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United Kingdom2025 Taiwan FDI Guide, Efficient Cross-Border Capital Management
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) serves as a crucial driver for Taiwan’s economic globalization and a key force propelling industrial upgrading, job creation, and technology transfer. Amid accelerating global capital flows, Taiwan continues attracting high-quality foreign capital, exerting profound impact on economic stability and innovative transformation.

What is “Foreign Direct Investment”?
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) refers to long-term investments where enterprises or individuals directly establish operations, acquire businesses, or obtain operational control overseas. Unlike indirect investments (e.g., stocks, bonds), FDI involves actual management control, typically used for setting up factories, mergers & acquisitions, or joint ventures. Such investments facilitate technology transfer, job creation, and local economic development, serving as a critical strategy for global expansion.
Foreign Direct Investment Advantages and Risk Analysis
Advantages of Foreign Direct Investment
FDI introduces capital, technology, and managerial expertise, enhancing local industrial competitiveness and employment rates. Simultaneously, it accelerates industrial upgrading and global integration while strengthening forex reserves and national credit standing serving as a vital engine for economic growth.
Risks of Foreign Direct Investment
FDI faces risks including exchange rate volatility, policy shifts, and cultural disparities. It may also create over-reliance on foreign capital or trigger local market monopolization. Investors must meticulously evaluate local environments and implement robust risk management.
FDI Impact on Taiwan and Future Trends
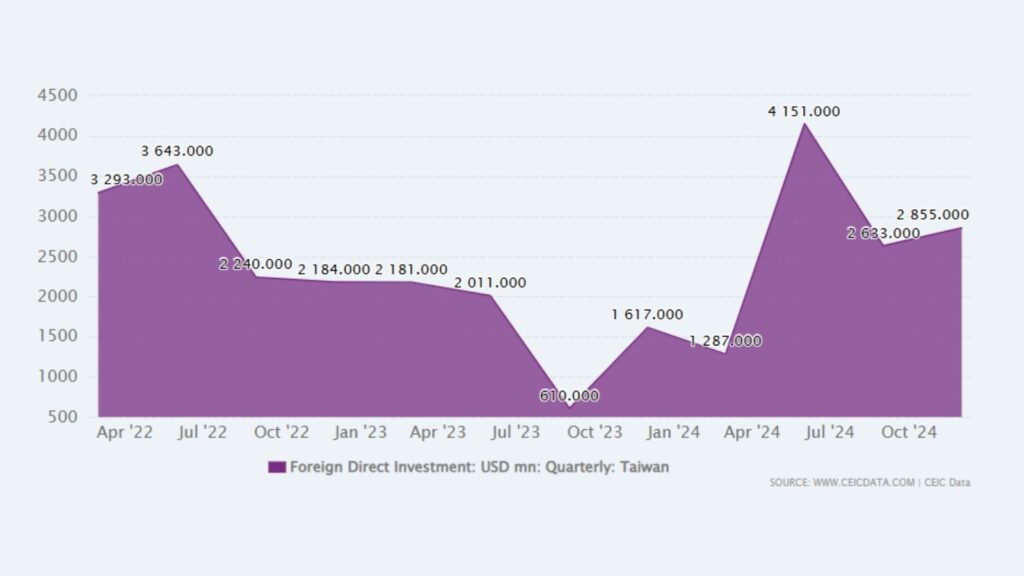
According to Taiwan’s Investment Commission data, January-April 2025 saw 642 approved FDI cases totaling USD 2.83 billion, a 66.7% YoY increase. Though case numbers dipped slightly, the capital surge indicates larger-scale investments, demonstrating Taiwan’s sustained appeal for major projects, particularly in tech services and green energy.
For instance: Amazon AWS announced establishing a new region in Taiwan, investing over USD 5 billion to build/operate data centers, enhancing local innovation particularly digital transformation capabilities. In 2024, TSMC partnered with Germany’s Bosch to establish an advanced packaging plant, creating over 2000 jobs and driving local supply chain upgrading. This underscores Taiwan’s strategic position in global FDI trends.
Taiwan FDI Procedures and Regulations
In Taiwan, FDI requires application to the Investment Commission MOEA. Key documents include:
- Investment proposal
- Capital source proof
- Shareholder structure disclosure
The process involves three steps:
- Proposal Approval: Submit to Investment Commission MOEA. Review focuses on fund source legitimacy and industry compliance.
- Company Setup & Capital Inflow: After approval, complete company registration, share registration, and capital remittance.
- Post-Operation Compliance: Report investment progress under Cross-Strait Relations Act and investment protection agreements.
Additionally, monitor legal risks like regulatory arbitrage, environmental audits, or divestment restrictions. Essential reference: Common FDI Legal Risks and Mitigation Strategies.
Successful FDI Strategies: Hedging and Value-Adding Techniques
To enhance investment returns, experts recommend adopting low-cost entry strategies for emerging markets in foreign direct investment. Core strategies include:
1. Diversified Investment Portfolio
When conducting FDI, enterprises and individuals should implement diversification strategies to spread country and industry risks. For example, avoiding concentrated exposure to single markets or high-volatility sectors reduces geopolitical/policy impacts on overall assets. Combining mature and emerging markets enhances investment stability and long-term return potential.
2. Utilize Hedging Tools for FX Risk Management
FDI involves cross-currency transactions where exchange fluctuations erode profits. Investors can lock conversion costs via hedging instruments like FX options or forward contracts. Selecting flexible risk control platforms (e.g., Ultima Markets) enables real-time exchange monitoring and risk management, optimizing capital allocation efficiency.
3. Target Value-Added Industries and Regions
Successful FDI prioritizes industry appreciation potential alongside capital returns. Focus on policy-supported, innovation-driven, or ESG-potential sectors like green energy tech and AI manufacturing. Concurrently, choose politically stable regions with transparent regulations and abundant talent to amplify long-term competitive advantages.
These strategies help enterprises and investors deploy foreign direct investment more robustly.

How to Start FDI with FX Trading Tools?
1. Assess Target Market and Industry Potential
Before FDI, conduct in-depth analysis of the target country’s economic fundamentals, industrial policies, and business environment. Utilize government data and international agency reports to evaluate growth potential and risk structures. Selecting industries with technological upgrade potential and government backing enhances investment returns while preventing resource misallocation.
2. Open International Trading Account & Establish Legal Entity
Successful FDI requires compliant and efficient financial/operational frameworks. Investors can open international trading accounts through professional brokers like Ultima Markets for seamless capital flow and FX settlement. Simultaneously, establish local entities or joint ventures per local laws to safeguard assets and leverage tax incentives.
3. Integrate FX Platform for Exchange Rate & Transfer Control
FDI involves large cross-border capital flows where exchange volatility directly impacts costs and returns. Platforms like Ultima Markets enable real-time quotes, risk hedging, and rapid transfers to mitigate FX loss risks, enhance capital allocation flexibility, and ensure robust investment execution.
If considering cross-border investments with FDI strategies, utilize CFD or FX platforms. Here, Ultima Markets emerges as the natural choice, offering:
- Regulated, Safe and Secure: Licensed by CySEC (Cyprus) and Mauritius FSC. Client funds insured up to $1,000,000 via Willis Towers Watson, covered under liability protection and financial dispute compensation fund.
- Low Threshold & Diverse Products: ECN Accounts, FX, indices, ETFs, crypto CFDs.
- Free Demo Account: Ideal for risk-free practice.
- Comprehensive Risk Controls: Segregated custody, negative balance protection, 24/7 monitoring.
For executing FDI and international trade barrier navigation strategies, UM serves as your essential toolkit for managing exchange rates, carry trades, and liquidity, optimizing global capital flows.
Register now for Ultima Markets demo account and personalized coaching to master international trading rhythms.
Conclusion
In 2025, global “Foreign Direct Investment” accelerates toward green energy and tech sectors, with Taiwan as a key beneficiary. After understanding markets through FDI procedures and regulations, combining CFD and FX trading using tools like Ultima Markets enables effective risk control and investment diversification.
This strategy implements low-cost entry into emerging markets via FDI, aligning with international capital deployment to chart your next-phase investment blueprint.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












