Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this websiteNasdaq Index: A Global Benchmark for Tech Investor
In today’s global investment landscape, if there’s one index that best represents innovation and growth, the Nasdaq Index undoubtedly stands out. As a hub for technology and new economy companies, it is not only one of the core indices of the U.S. market but also a crucial benchmark for global investors to assess risk and identify opportunities. This article starts with the fundamentals, offering a comprehensive understanding of the Nasdaq Index’s composition, operational logic, trading methods, and practical applications—while also explaining how to leverage the advantages of the Ultima Markets platform for flexible execution.
What is the NASDAQ Composite Index? Decoding Market Trends Through US Tech Dynamics
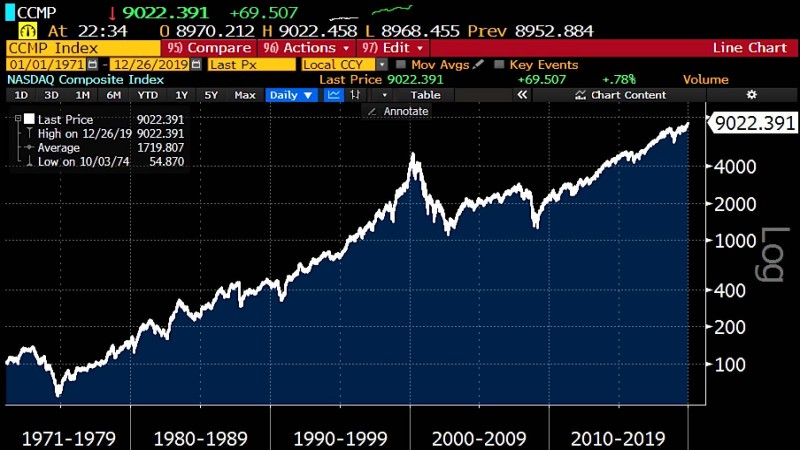
The NASDAQ Composite Index, established in 1971 and maintained by the NASDAQ Stock Exchange, tracks over 3,000 listed companies, making it the world’s largest equity index by constituent count. This market capitalization-weighted benchmark predominantly features high-growth sectors including technology, semiconductors, biotechnology, artificial intelligence, digital media, and cloud computing.
Compared to the Dow Jones Industrial Average and S&P 500, the NASDAQ Composite demonstrates heightened sensitivity to New Economy shifts. Its components – including Apple, Microsoft, NVIDIA, Amazon, and Alphabet (Google’s parent company) – represent global industry leaders. This positions the index as a critical barometer for assessing worldwide tech sector performance.
NASDAQ Composite Index Components and Sector Structure
The NASDAQ Composite Index comprises over 3,000 stocks, with over 50% of its market capitalization concentrated in Information Technology, E-Commerce, and Digital Media sectors. Below is a simplified breakdown of key sector allocations and representative companies:
| Sector | Market Cap Allocation | Representative Companies |
| Information Technology | 50% | Apple, Microsoft, NVIDIA |
| Communication & Digital Media | 20% | Google, Meta |
| E-Commerce | 10% | Amazon |
| Biotechnology & Pharmaceuticals | 10% | Amgen, Moderna |
| Others | 10% | Tesla, Adobe |

Nasdaq Index Futures & ETFs: Flexible Market Participation Channels
Beyond traditional stock trading, investors can access Nasdaq index movements through futures, ETFs, or CFDs. Ultima Markets offers diversified instruments for both short-term traders and long-term allocators.
Comparison of common access methods:
| Instrument | Liquidity | Fee Structure | Flexibility | Target Users |
| Nasdaq Futures | High | Exchange spreads | Leverage available | Professional traders |
| Nasdaq ETFs | High | Low expense ratios | Ease of use | Long-term investors |
| CFDs | High | Platform spreads | High leverage | Active traders |
Through Ultima Markets, investors can activate trading accounts to customize leverage ratios, apply technical indicators, and synthesize real-time market data for swift volatility exploitation.
NASDAQ Composite vs. S&P 500: Core Differential Analysis
While both represent core US equity benchmarks, the NASDAQ Composite and S&P 500 differ fundamentally in composition and market representation:
| Metric | NASDAQ Composite | S&P 500 |
| Constituent Count | Constituent Count | 500 constituents |
| Sector Bias | Tech & innovation focus | Broad sector diversification |
| Volatility Profile | Higher | More stable |
| Inclusion Criteria | No profitability requirements; listing status sufficient | Proven profitability & market capitalization thresholds |
The NASDAQ Composite more directly captures the growth trajectory of tech innovation enterprises, whereas the S&P 500 offers a macroeconomic barometer of the US economy’s holistic health.
How to Trade the NASDAQ Index via Ultima Markets?
Ultima Markets delivers comprehensive index trading solutions including:
Real-time quotes & multi-currency funding
Customizable leverage ratios & risk controls
Platform diversity: MT4, WebTrader, mobile apps
Demo accounts for strategy testing
Daily market analysis reports for informed decisions
Whether you’re a short-term technical trader or a cost-conscious long-term investor, Ultima Markets equips you with precision tools for NASDAQ index exposure.
FAQ: NASDAQ Index Investment FAQs
Q1: Is investing in the NASDAQ Composite high-risk?
A: While exhibiting higher volatility, the NASDAQ demonstrates strong long-term performance. Mitigate risks via stop-loss strategies and risk asset allocation.
Q2: Can small investors access NASDAQ index exposure?
A: Absolutely. ETFs and CFDs enable low-entry investments, complemented by dollar-cost averaging for gradual position building.
Q3: How does NASDAQ Composite differ from NASDAQ-100?
A: NASDAQ-100 tracks the index’s 100 largest-cap firms with lower volatility and concentrated exposure. The Composite includes all listed stocks for broader representation.
Q4: Should I trade ETFs or CFDs?
A: Depends on strategy and risk tolerance. ETFs suit passive holding; CFDs offer flexibility for swing/day trading.
Q5: What investor profile fits NASDAQ index exposure?
A: Those with market acuity seeking tech growth dividends while managing volatility risks.
Conclusion: The NASDAQ Composite Mirrors Long-Term Technological Evolution
The NASDAQ Composite transcends stock price aggregation, serving as a microcosm of global tech innovation. Integrating it into portfolios through optimal instruments enhances return potential while providing strategic positioning against future disruptions.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












