
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomBitcoin mining is the process through which transactions are verified and added to the public ledger, the blockchain. It also serves as the mechanism by which new bitcoins are introduced into circulation. Bitcoin mining involves solving complex cryptographic puzzles, and miners are rewarded with new bitcoins for validating transactions. Understanding what Bitcoin mining is and how it works is essential for beginners who wish to participate in or learn about the Bitcoin network.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining refers to the process by which Bitcoin transactions are verified and added to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve cryptographic puzzles and, upon solving the puzzle, they validate a block of transactions. Miners are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees as compensation.
- Bitcoin’s Proof of Work mechanism is central to mining, ensuring the security of the network and the creation of new blocks in the blockchain.
- Bitcoin’s supply is capped at 21 million coins, making the mining process essential to both the creation of new bitcoins and the integrity of the network.
Key Aspects of Bitcoin Mining:
- Mining Hardware: High-powered computers (ASIC miners) are used for solving cryptographic puzzles.
- Mining Reward: Currently, miners are rewarded 6.25 bitcoins per block, but this decreases over time due to the “halving” events.
- Mining Pools: Miners often join pools to increase their chances of solving blocks and earning rewards.

How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Bitcoin mining involves several steps to ensure the secure validation of transactions. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Transaction Verification: Bitcoin miners verify unconfirmed transactions within the Bitcoin network. Transactions consist of details like the sender, receiver, and amount of Bitcoin to be transferred.
- Block Creation: After verification, miners group transactions into a “block.” The goal is to validate and secure this block.
- Solving the Cryptographic Puzzle: Miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle, a process that requires significant computational power. The first miner to solve the puzzle adds the block to the blockchain.
- Mining Reward: Once the block is added to the blockchain, the miner receives a reward in the form of newly minted Bitcoin and transaction fees.
- Proof of Work (PoW): Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism is called Proof of Work. Miners must show proof that they have expended computational resources to solve a puzzle, securing the network from fraudulent transactions.
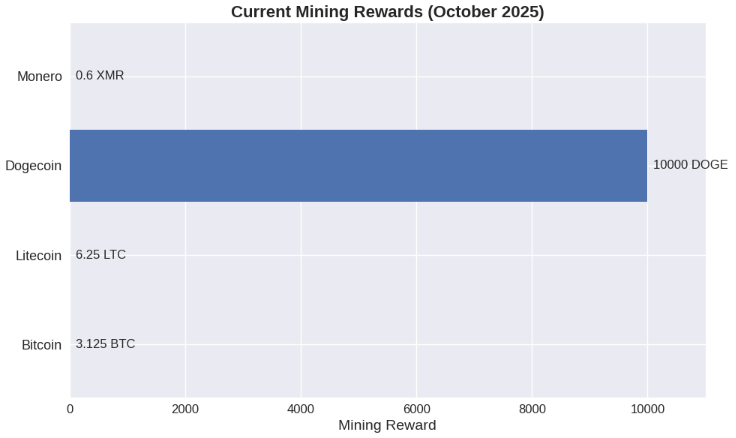
Mining Rewards Overview (October 2025)
- Bitcoin: Halved in April 2024, now at 3.125 BTC per block.
- Litecoin: Currently rewards 6.25 LTC per block, with its next halving expected in 2027.
- Dogecoin: Uses a fixed reward system of approximately 10,000 DOGE per block.
- Monero: Offers a dynamic reward, currently around 0.6 XMR per block.
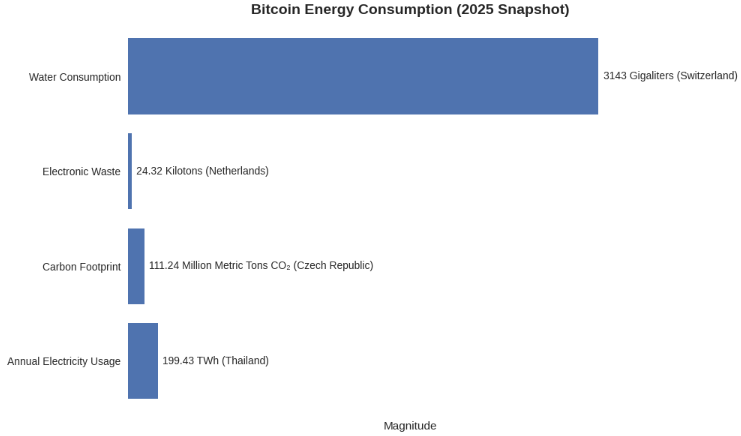
Bitcoin Energy Consumption (2025 Snapshot)
- Annual electricity usage: 199.43 TWh. Equivalent to the power consumption of Thailand.
- Carbon footprint: 111.24 million metric tons of CO₂. Comparable to the emissions of the Czech Republic.
- Electronic waste: 24.32 kilotons. Similar to the small IT equipment waste of the Netherlands.
- Water consumption: 3,143 gigaliters. Roughly equal to the total water use of Switzerland
What are the Economics of Mining Bitcoin?
The economics of mining Bitcoin are affected by several factors, including hardware costs, electricity prices, and Bitcoin’s market value. Here’s a breakdown:
Mining Hardware Costs:
Bitcoin mining requires specialized hardware, known as ASIC miners. These are more efficient and powerful than regular computers or GPUs, but they come with a high initial investment.
Electricity Costs:
Mining consumes vast amounts of electricity, which makes it expensive. Miners tend to set up operations in areas where electricity is cheap, such as in regions with abundant natural energy sources.
Bitcoin Price and Market Volatility:
The profitability of mining is heavily tied to Bitcoin’s market price. A rising Bitcoin price makes mining more profitable, whereas a falling price can make it less economical.
Block Reward and Mining Difficulty:
Currently, miners receive 6.25 BTC per block as a reward. This reward is halved approximately every four years, reducing the amount of new Bitcoin released into circulation. The difficulty of mining also adjusts every 2,016 blocks to ensure that blocks are mined approximately every 10 minutes.
Issues with Bitcoin Mining
While Bitcoin mining offers rewards, it also comes with significant challenges:
- Environmental Impact: Bitcoin mining is energy-intensive, leading to concerns about its environmental footprint. Many mining operations rely on non-renewable energy sources, contributing to carbon emissions.
- Centralization of Mining: Over time, Bitcoin mining has become concentrated within large mining pools. This could potentially undermine the decentralized nature of the Bitcoin network.
- Security Risks: Mining operations are susceptible to cyberattacks, including hacking and phishing attempts. Miners must take significant precautions to secure their networks and systems.
- Regulatory Challenges: Some countries have imposed bans or restrictions on Bitcoin mining due to concerns about energy consumption and financial risks. It’s important to stay informed about the regulatory environment in your country or region.
Avoid Bitcoin Mining Scams
As Bitcoin mining has grown in popularity, scams have proliferated. Here are some red flags to watch out for:
- Cloud Mining Scams: These services promise high returns with little investment but often turn out to be Ponzi schemes. Avoid cloud mining services that make unrealistic promises.
- Fake Hardware Sales: Be cautious when purchasing mining hardware. Scammers may sell outdated or inefficient equipment that can’t generate a reasonable return.
- Phishing Scams: Fraudulent websites and emails often impersonate legitimate Bitcoin services to steal personal information or funds. Always verify the authenticity of websites and emails.
To avoid falling victim to scams:
- Research: Always verify mining services and hardware through reputable reviews and feedback.
- Watch Out for Unrealistic Promises: If an offer sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
- Trust Verified Platforms: Stick to well-known platforms with a proven track record in the industry.
Investing in Bitcoin Mining Stocks
If direct mining isn’t for you, you can invest in companies involved in Bitcoin mining or related sectors. These companies manage mining operations, produce mining hardware, or offer financial products related to Bitcoin.
Some notable Bitcoin mining stocks include:
- Riot Blockchain (RIOT)
- Marathon Digital Holdings (MARA)
- Hut 8 Mining Corp (HUT)
Investing in Bitcoin mining stocks offers exposure to the mining industry without the need for physical mining equipment. However, stock prices can be volatile, so it’s essential to conduct thorough research before investing.
Conclusion
Both Bitcoin mining and Bitcoin trading are integral parts of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, but they cater to different types of participants and offer varying levels of involvement, risk, and reward.
Bitcoin mining is a resource-intensive process that requires substantial hardware investment, electricity, and technical know-how. It’s a long-term commitment, with miners relying on their computational power to secure the network and earn rewards in the form of newly minted bitcoins. The mining process is deeply intertwined with Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, offering the opportunity to participate in the creation of new coins, but it also comes with environmental concerns and regulatory challenges.
On the other hand, Bitcoin trading is a more accessible avenue for individuals looking to profit from Bitcoin’s price volatility. Traders can buy and sell Bitcoin on exchanges, utilizing various strategies such as day trading, swing trading, or long-term investing. While trading requires less upfront capital compared to mining, it comes with its own set of risks, especially given Bitcoin’s volatile nature. For those interested in Bitcoin but not willing to engage in the complexities of mining, trading offers a more flexible option.
Whether you’re considering investing in Bitcoin mining stocks or diving into the world of Bitcoin trading, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the risks and rewards involved. Both avenues can be lucrative, but each requires careful research and a solid risk management strategy.
By staying informed, avoiding scams, and developing a strategic approach, you can navigate the world of Bitcoin confidently whether you’re mining for coins or trading on the market.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












