
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomWhat Is Mirror Trading?
Mirror trading is an automated investing method where your account replicates a strategy’s trade signals in (near) real time. It began in FX in the early 2000s and was popularised by platforms such as Tradency’s Mirror Trader (launched in 2005) before spreading to broader markets.
Mirror trading vs. copy/social trading:
- Mirror trading traditionally follows a predefined strategy (a rules-based model).
- Copy trading usually follows a specific trader’s orders and may be treated as portfolio management by regulators if there’s no manual client input. ESMA and the UK FCA have clarified how firms offering these services should be supervised and authorised.
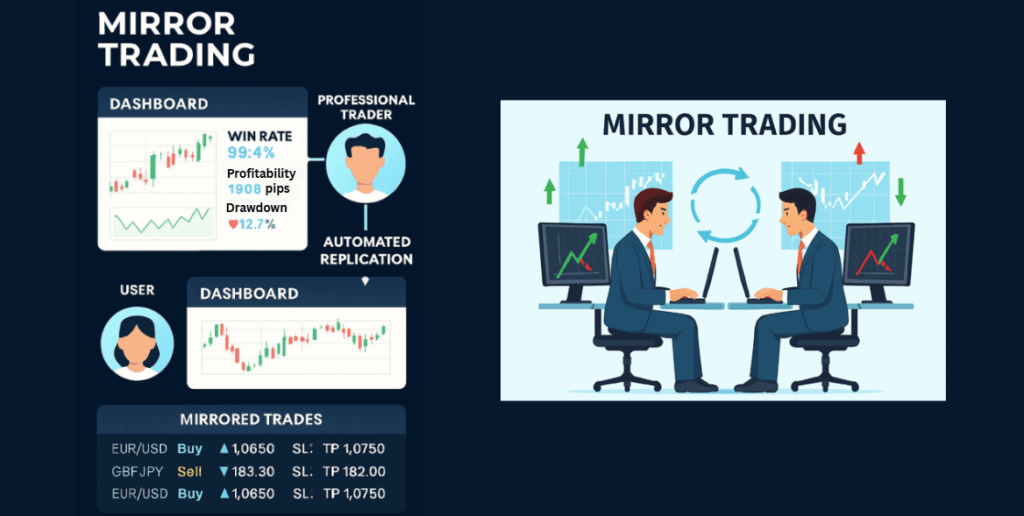
How Mirror Trading Works
Mirror trading operates through an automated link between your trading account and a chosen strategy provider. Once you select a strategy, the system automatically replicates every buy or sell signal generated by that strategy in your own account, no manual execution required. This process allows traders to mirror the decisions of experienced professionals or algorithmic systems in real time, providing the same market exposure and outcomes in proportion to their allocated capital.
Unlike manual or discretionary trading, mirror trading relies on automation, transparency, and consistency, making it especially useful for traders who want to follow proven strategies or diversify without constant screen time. The overall mechanism can be broken down into several key steps:
- Select a platform & strategy: Platforms list strategies with performance and risk metrics (e.g., win rate, max drawdown, Sharpe, followers, history length).
- Configure risk: Set allocation method (fixed or proportional), leverage caps, daily loss limits, and max open trades. ESMA notes some models let clients modify or reject copied orders; others are fully automated.
- Auto-execution: When the source strategy trades, your account places the same (or proportional) order. Latency, liquidity, and spreads create slippage between master and follower fills.
- Monitor & rotate: Review live results, re-weight allocations, and pause/replace strategies that breach your risk rules. International regulators (ESMA/IOSCO) emphasise suitability and clear disclosures for these services.
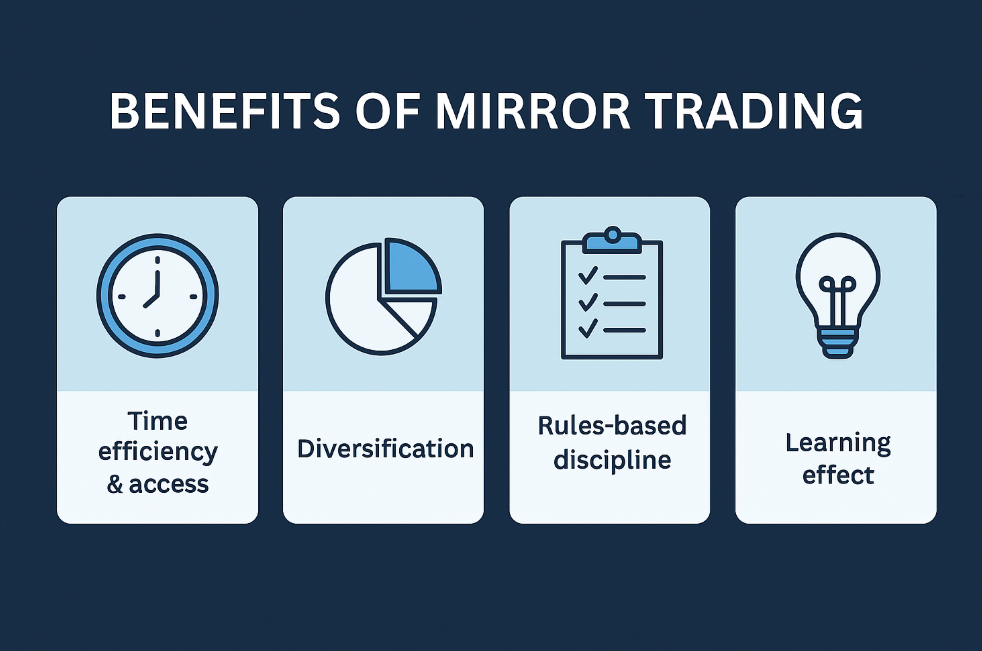
Benefits of Mirror Trading
The main advantage of mirror trading lies in its ability to combine automation with expert-level decision-making. By linking your account to professional strategies, you gain exposure to market opportunities without needing to analyse charts or react to every price swing yourself. This form of automated trading allows investors to learn from proven systems, maintain discipline during volatile conditions, and diversify across multiple markets, all while keeping control of their risk parameters.
Here are some of the key benefits of mirror trading that make it increasingly popular among modern traders:
- Time efficiency & access: Follow systematic or professional-grade models without building them yourself.
- Diversification: Allocate across uncorrelated strategies (trend, mean-reversion, carry, volatility) to smooth your equity curve.
- Rules-based discipline: Automation reduces emotional errors and enforces consistent risk limits.
- Learning effect: Reviewing live signals helps you understand entries, exits, and risk control used by experienced developers.
Risks and Challenges of Mirror Trading
While mirror trading offers convenience and access to professional strategies, it also comes with important risks that every trader should understand. Automated replication of trades means both profits and losses are mirrored in real time, leaving little room for emotional intervention once positions are open. Performance can vary depending on market conditions, execution speed, and the quality of the underlying strategy. In addition, traders must consider regulatory oversight, platform reliability, and hidden costs that may affect long-term profitability.
To manage expectations and avoid common pitfalls, it’s essential to be aware of the following risks and challenges of mirror trading:
- Regulatory & suitability duties: In the UK, copy/mirror services with no client input often qualify as portfolio/investment management; providers must be authorised and meet suitability/appropriateness obligations. ESMA’s 2023 supervisory briefing sets expectations for EU firms.
- Execution risk: Latency and liquidity can cause slippage; thin markets and high volatility widen differences from the master account’s fills.
- Strategy decay & selection bias: Backtests can be overfit; insist on robust live track record and scrutinise max drawdown. IOSCO highlights retail harm potential when investors don’t fully grasp automated risk.
- Fees & platform risk: Complex fee stacks (spread, commission, performance/copy fees) can erode returns; outages and weak controls add operational risk. The FCA’s Dec 13, 2024 Dear Portfolio letter lists harm drivers in the CFD sector and supervisory priorities through 2026.
- Model confusion: Services marketed as “copy/mirror” might actually be PAMM/MAM allocations. Verify what you’re signing up for and how orders are routed. ESMA/IOSCO stress clear disclosures and qualifications of “signal providers.”
Choosing the Right Mirror Trading Platform
- Authorisation & jurisdiction fit – Verify the firm on the official register (e.g., FCA Financial Services Register in the UK). Understand if the service is classed as portfolio management and what protections apply.
- Transparent, verifiable performance – Look for clearly presented max drawdown, sample size, history length, and independent verification where possible.
- Client controls – Ability to set loss caps, max open trades, leverage limits, and to pause/reject signals where supported.
- Costs in plain English – Total cost = spreads + commissions + copy/performance fees + conversion/overnight costs. FCA expects fair, clear, non-misleading disclosures for CFD-related services.
- Operational resilience – Uptime, incident reporting, client money segregation, and best-execution monitoring.
- Education & risk warnings – ESMA/IOSCO expect firms to provide clear risks and investor education for copy/mirror trading.
Mirror Trading Strategies
- Trend-Following – Rides directional moves; vulnerable to chop.
- Mean-Reversion/Range – Fades extremes; needs strict risk control during breakouts.
- Carry (FX) – Harvests rate differentials, sensitive to central-bank shifts and risk-off shocks.
- Breakout/Volatility – Enters on range expansions thrives in high volatility, whipsaws in false breaks.
- Intraday/Scalping – Many small trades highly dependent on execution quality and latency.
Start small (e.g., 10–20% of risk capital) across 2–4 lower-correlated strategies. Pause any model that exceeds 1.5× its historical max drawdown and re-underwrite quarterly.
Is Mirror Trading Legal?
Yes, it is legal when offered by authorised firms and in line with local rules. In the UK/EU, many offerings are treated as portfolio management or other MiFID II services, which impose suitability and disclosure duties on providers.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-moving financial markets, mirror trading has become a bridge between professional and retail investing, allowing everyday traders to benefit from expert strategies without needing to trade manually. Whether applied in forex trading, crypto trading, or commodities, this approach offers the power of automation, diversification, and data-driven decision-making.
However, automation doesn’t eliminate risk. Each strategy carries potential drawdowns, execution differences, and exposure to market volatility. The key is to choose regulated brokers, verify the transparency of each strategy provider, and apply strong risk management controls.
Used wisely, mirror trading can complement a balanced trading plan, giving you exposure to different asset classes while maintaining structure and discipline. But just like any form of automated trading, success depends on continuous oversight, realistic expectations, and a solid understanding of how each strategy performs under real market conditions.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












