Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this websiteIn the world of options trading, the Bear Call Spread is a popular strategy used to profit from neutral to bearish market conditions. By combining the sale of a lower strike call with the purchase of a higher strike call, traders can create a limited risk, limited reward position that thrives when the underlying asset remains below a certain price.
What is a Bear Call Spread?
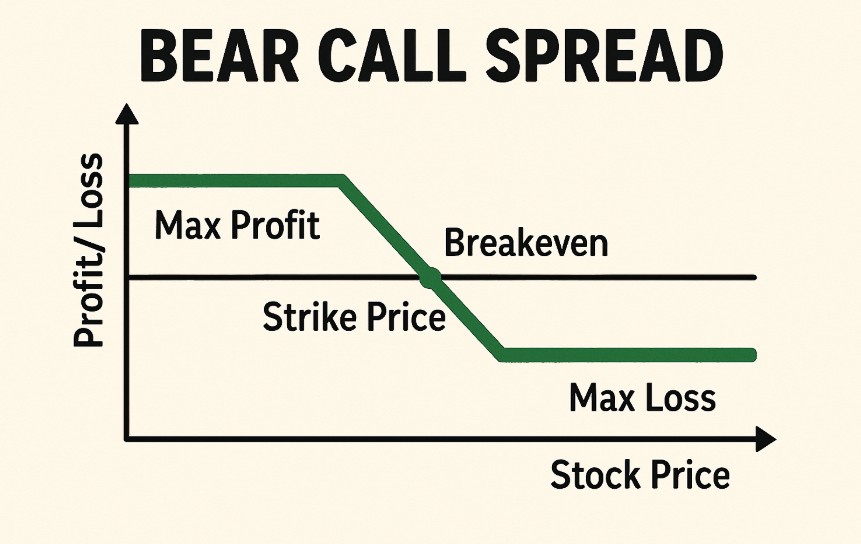
A Bear Call Spread is an options trading strategy designed to profit from a neutral to bearish market outlook. It involves selling a call option at a lower strike price while simultaneously buying a call option at a higher strike price, both with the same expiration date. This creates a credit spread, where the trader receives a premium for selling the call and pays a smaller premium for the call option bought for protection.
This strategy is primarily used when traders expect the price of the underlying asset to either stay flat or experience a slight decline. The Bear Call Spread has limited risk and limited reward, making it an ideal choice for those seeking to capitalize on market stagnation or moderate declines.
When to Use a Bear Call Spread
The Bear Call Spread is ideal in the following market conditions:
- Neutral to Bearish Market: If you believe that the underlying asset will not experience significant price growth or will decline, this strategy allows you to profit.
- Limiting Risk: Unlike selling a naked call, a Bear Call Spread limits the trader’s risk since the long call option acts as protection.
- Range-Bound Market: This strategy is best suited for markets where the asset’s price is expected to stay within a specific range, not breaking through the strike price of the sold call option.
Bear Call Spread Strategy Explained
The Bear Call Spread is a limited risk, limited reward strategy. Here’s how it works:
- Sell a Call Option: You sell a call option at a lower strike price, generating premium income.
- Buy a Call Option: Simultaneously, you buy a call option with a higher strike price, which limits your potential losses.
- Expiration Date: Both options expire on the same date.
Risk and Reward
- Maximum Profit: The maximum profit occurs when the underlying asset stays below the sold call’s strike price. The maximum profit is the net premium received for the spread.
- Maximum Loss: The maximum loss is the difference between the strike prices minus the net premium received. This happens if the asset’s price rises above the higher strike price.
Bear Call Spread Example
These two examples demonstrate the Bear Call Spread strategy applied to both a tech stock and an ETF.
Example 1: Tech Stock – Apple (AAPL)
Market Outlook: You believe Apple’s stock (AAPL) will remain below $150 in the next month due to upcoming earnings concerns or market volatility.
Step 1: Sell a call option with a strike price of $150 for a premium of $5.
Step 2: Buy a call option with a strike price of $155 for a premium of $2.
Net Premium Received: $5 (received) – $2 (paid) = $3 per share.
Profit and Loss:
- Maximum Profit: If AAPL stays below $150 at expiration, you keep the $3 premium per share as profit.
- Maximum Loss: If AAPL rises above $155, your loss is capped at the difference between the strike prices ($155 – $150 = $5) minus the premium received ($3). Therefore, the maximum loss is $2 per share.
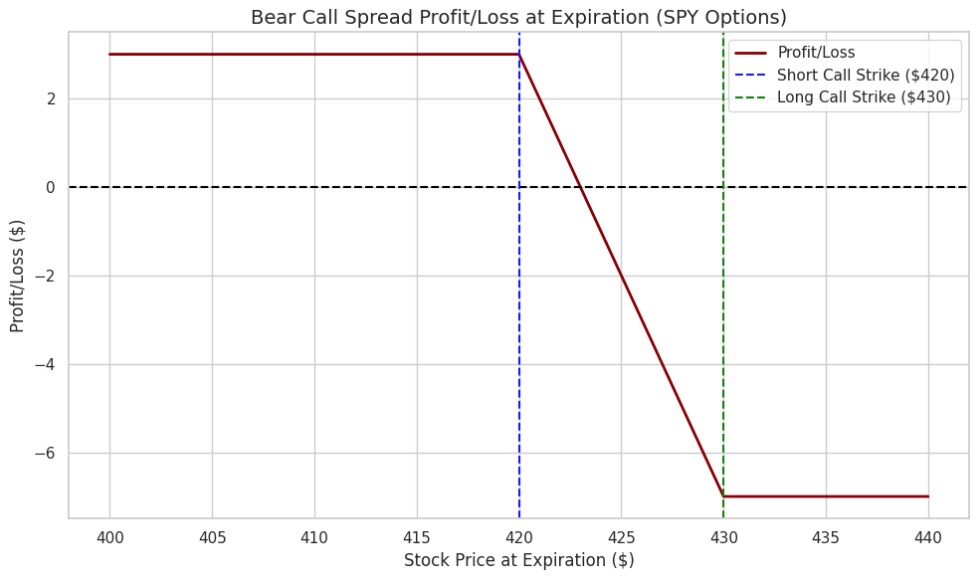
Example 2: ETF – SPY (S&P 500 ETF)
Market Outlook: You expect the S&P 500 ETF (SPY) to remain below $420 in the near term due to market concerns, and you believe it won’t rally significantly.
Step 1: Sell a call option with a strike price of $420 for a premium of $4.
Step 2: Buy a call option with a strike price of $430 for a premium of $1.
Net Premium Received: $4 (received) – $1 (paid) = $3 per share.
Profit and Loss:
- Maximum Profit: If SPY stays below $420 at expiration, you keep the $3 premium as profit.
- Maximum Loss: If SPY rises above $430, your loss is capped at the difference between the strike prices ($430 – $420 = $10) minus the premium received ($3). Therefore, the maximum loss is $7 per share.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bear Call Spread
Advantages:
- Limited Risk: One of the main benefits of this strategy is the limited risk. The maximum loss is capped, unlike selling a naked call where the loss potential is theoretically unlimited.
- Profit in Neutral Markets: The Bear Call Spread allows traders to profit in markets that are either neutral or bearish, where the price doesn’t rise significantly.
- Simple Execution: The strategy involves only two positions, which makes it easier to manage compared to multi-leg strategies such as the Iron Condor.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Profit Potential: The maximum profit is restricted to the net premium received, which means you can’t benefit from large price movements.
- Requires Accurate Market Prediction: The strategy requires a fairly accurate forecast of the asset’s price movement. If the asset rises above the higher strike price, the strategy incurs losses.
- Margin Requirements: Even though the strategy is limited in risk, brokers may require higher margin requirements due to the short position taken in the strategy.
Difference Between Bear Put Spread and Bear Call Spread
While both strategies are designed for bearish market conditions, they have key differences:
Market Outlook:
- A Bear Call Spread profits when the asset’s price stays below the strike price of the sold call, with moderate decline or stagnation.
- A Bear Put Spread profits when the asset’s price falls significantly below the purchased put’s strike price.
Strategy Setup:
- A Bear Call Spread involves selling a lower strike call and buying a higher strike call.
- A Bear Put Spread involves buying a higher strike put and selling a lower strike put.
Risk/Reward:
Both strategies limit risk, but the Bear Call Spread has a max loss that is the difference between the strikes minus the premium received. The Bear Put Spread has a max loss that is similar but involves a different setup with puts.
Conclusion
The Bear Call Spread is an excellent strategy for traders who anticipate a neutral to bearish market and want to profit with limited risk. It’s most effective when the price of the underlying asset is expected to remain below the sold call’s strike price. The strategy is particularly useful for conservative traders seeking to profit from range-bound markets or small declines in the price of an asset.
While the maximum profit is limited, the maximum loss is also capped, making the Bear Call Spread a safer alternative to more aggressive strategies like naked call selling. If you’re new to options or looking for a defined risk/reward profile, the Bear Call Spread can be a great tool in your trading arsenal.
Interested in learning more about options strategies like the Bear Call Spread? Join Ultima Markets today for expert insights, strategies, and educational resources to enhance your trading skills.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.