Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomThe strength or weakness of a country’s currency plays a major role in global trade, investments, and travel costs. In 2025, several nations have currencies that are valued lower than the Indian Rupee (INR), reflecting differences in economic stability, inflation rates, and monetary policies.
Knowing which country currency is lower than India not only helps travelers budget effectively but also gives traders insights into forex market trends. This guide explores the world’s lowest currencies vs the Indian Rupee, why traders monitor weak currencies, and what these valuations mean for global market opportunities.
Which Country Currency Is Lower than India? Top 20 List
The list below shows the top 20 currencies weaker than the Indian Rupee based on mid-market rates in August 2025.
| Rank | Currency — Country | Units per 1 INR (approx.) | Notes |
| 1 | Iranian Rial (IRR) | ~480–490 IRR | Persistent high inflation and sanctions weigh heavily on value. |
| 2 | Vietnamese Dong (VND) | ~299–308 VND | Stable but long-standing low denomination due to historical inflation. |
| 3 | Sierra Leonean Leone (SLL) | ~260–263 SLL | Currency redenominated in 2022; still pressured by low export revenues. |
| 4 | Laotian Kip (LAK) | ~246–253 LAK | Weak demand and reliance on imports keep it undervalued. |
| 5 | Indonesian Rupiah (IDR) | ~186–190 IDR | Large money supply and low per-unit value despite economic growth. |
| 6 | Uzbekistani Som (UZS) | ~142–153 UZS | Gradual liberalisation hasn’t lifted the currency’s unit value much. |
| 7 | Guinean Franc (GNF) | ~99–101 GNF | Commodity-driven economy vulnerable to price swings. |
| 8 | Paraguayan Guarani (PYG) | ~82–95 PYG | Low global demand for the currency keeps nominal value small. |
| 9 | Cambodian Riel (KHR) | ~45–47 KHR | Widely overshadowed by the US dollar in domestic use. |
| 10 | Ugandan Shilling (UGX) | ~40–41 UGX | Agricultural dependency and trade deficits keep it weak. |
| 11 | Malagasy Ariary (MGA) | ~55–60 MGA | Limited export diversity, import reliance. |
| 12 | Congolese Franc (CDF) | ~33–36 CDF | Political instability, weak institutions. |
| 13 | Tanzanian Shilling (TZS) | ~29–31 TZS | Persistent trade imbalance. |
| 14 | Nepalese Rupee (NPR) | ~1.60 NPR | Pegged to INR at a fixed rate; weaker by policy. |
| 15 | Burundian Franc (BIF) | ~33–35 BIF | Inflationary pressures, limited reserves. |
| 16 | Zambian Kwacha (ZMW) | ~0.26–0.27 ZMW | Debt stress, currency depreciation. |
| 17 | Myanmar Kyat (MMK) | ~25–28 MMK | Political turmoil, FX restrictions. |
| 18 | Syrian Pound (SYP) | ~1,300–1,400 SYP | Conflict-driven collapse, sanctions. |
| 19 | Lebanese Pound (LBP) | ~1,020 LBP | Banking crisis, hyperinflation. |
| 20 | Zimbabwean Dollar (ZWL) | Illiquid / parallel rates vary | Hyperinflation, dual currency system. |
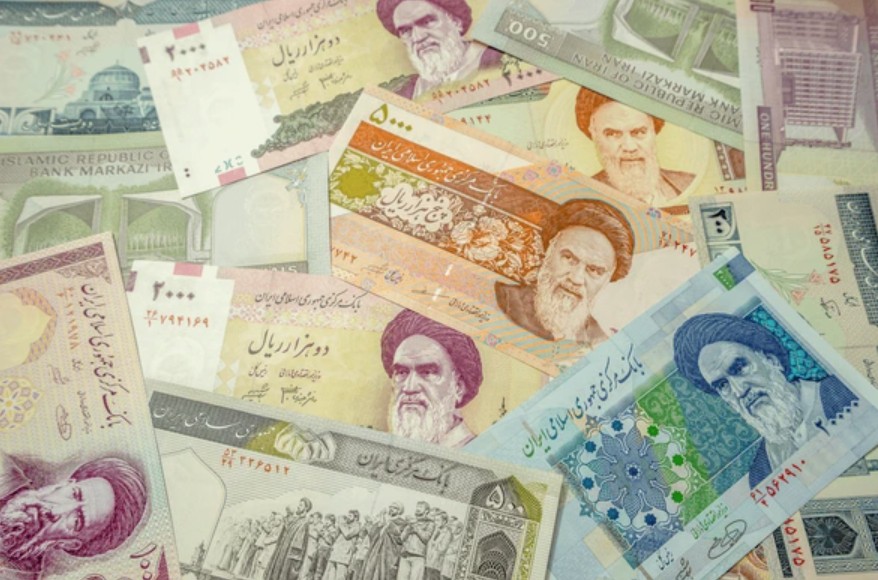

World Lowest Currency vs Indian Rupee
The world’s lowest currency vs Indian Rupee refers to the currency that has the highest number of units required to equal 1 INR. As of 2025, that title belongs to the Iranian Rial (IRR), where roughly 480–490 IRR equals 1 INR.
However, it’s important to understand that “lowest” here doesn’t mean “worst” in all cases, it simply means the currency has a very low per-unit value in the foreign exchange market. This low nominal value is usually the result of:
- Hyperinflation — rapid price increases erode currency value.
- Monetary policy decisions — such as printing more money to cover deficits.
- Political and economic instability — which drives investors away and reduces demand for the currency.
- Exchange rate pegs or re-denominations — sometimes lowering the unit value intentionally.
From a market standpoint, the world’s lowest currency vs Indian Rupee is not automatically a buy signal. In many cases, such currencies:
- Face capital controls that limit convertibility.
- Have low liquidity, making it hard to execute trades.
- Can lose value even faster if economic reforms fail.
For example, the Iranian Rial, Lebanese Pound, and Syrian Pound all trade at very high nominal rates against the INR, but they also have high inflation and market restrictions, making speculative trading risky.

Weak Currency Is Good Invest?
In most cases, no. A weak currency is usually a sign of economic stress, and without a clear, credible recovery plan, its value may keep falling. Even if you can buy large amounts cheaply, the real purchasing power and ease of conversion matter more than the face value.
Professional traders may target weak currencies for short-term speculative moves or hedging strategies, but long-term holding is high-risk.
Why Traders Monitor Weak Currencies
Traders closely monitor weak currencies because they can present both trading opportunities and economic signals that influence the broader market. Here are the main reasons:
Arbitrage and Forex Volatility Opportunities
Weak currencies often experience high volatility due to frequent exchange rate fluctuations. For forex traders, this volatility can lead to larger price swings in shorter timeframes, creating potential profit opportunities. For example, if the Iraqi Dinar or Iranian Rial moves significantly against the Indian Rupee, a skilled trader could take advantage of the spread.
Carry Trade Potential
Some weak currencies come with higher interest rates due to inflation and economic instability. Traders may engage in carry trades, borrowing in a low-interest currency and investing in a high-interest one to capture the rate differential. However, this carries higher risk due to potential currency depreciation.
Economic & Political Risk Assessment
A currency’s weakness often reflects a country’s economic health, inflation rate, and political stability. Traders analyze these currencies to understand underlying market risks. For example, persistent weakness may indicate fiscal deficits, sanctions, or a struggling export sector.
Impact on Commodities and Trade
Countries with weaker currencies often have cheaper exports in the global market. This can influence commodity prices. For instance, a weak currency in an oil-exporting country may lead to changes in crude pricing strategies, impacting global trade and commodity traders.
Hedging Strategies
Investors and companies with exposure to weak-currency nations may use forex hedging to protect against further depreciation. Traders monitor these movements to time entry and exit points for hedging instruments.
In short, weak currencies are not just a sign of economic trouble, they are key indicators for market trends and trading strategies. Professional traders treat them as part of a larger macroeconomic puzzle, helping them forecast market movements and adjust portfolios accordingly.
Conclusion
Understanding which country currency is lower than India in 2025 helps traders, investors, and even travelers make informed financial decisions. By analyzing the world’s lowest currencies vs the Indian Rupee, traders can spot potential opportunities in forex markets, assess the impact of inflation and monetary policy, and anticipate market volatility.
While a weak currency may present attractive trading setups, it often reflects deeper economic challenges that require careful risk management. With the right market analysis, tools, and guidance from a trusted broker like Ultima Markets, traders can navigate currency movements effectively and capitalize on global forex opportunities.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.