
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomWhat Is Spot Trading?
Spot trading is the purchase or sale of a financial asset for immediate delivery, with transactions typically settled “on the spot” or within two business days. This type of trading occurs on spot markets, where prices reflect the real-time value of an asset.
Unlike futures or options contracts that lock in future delivery prices, spot trading involves the instant exchange of assets at current market prices.
Examples of spot markets include:
- Forex spot market: Buying or selling currencies like EUR/USD or USD/JPY at current rates.
- Crypto spot trading: Purchasing digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum on exchanges.
- Commodities spot market: Trading gold, oil, or silver for immediate delivery.

How Does Spot Trading Work?
Spot trading works through order matching on centralized or decentralized exchanges. A trader places a buy or sell order at the desired price, and the system matches it with a counterparty willing to take the opposite position.
Key features:
- Market Orders: Execute instantly at the best available price.
- Limit Orders: Execute only at a specific price or better.
- T+2 Settlement: In traditional markets (e.g., forex), trades settle within two business days.
Spot prices are driven by supply and demand, economic news, interest rates, geopolitical events, and macroeconomic data. Traders often use technical indicators and economic calendars to time their trades.
Why Do People Trade Spot Markets?
Traders prefer spot trading for its simplicity, transparency, and lower risk profile compared to leveraged instruments. Here are key reasons:
- Direct asset ownership: Traders actually hold the asset (e.g., crypto coins, physical gold, or base currency).
- No rollover fees: Unlike margin trading, spot positions don’t incur overnight funding costs.
- Transparency: Spot prices reflect true market sentiment in real time.
- High liquidity: Especially in major forex pairs and crypto assets.
For long-term investors or conservative traders, spot trading provides a cleaner exposure to price movement without added complexity.
Types of Spot Trading Markets
Spot trading is available across multiple financial markets. Each market has unique characteristics, but they all share the core principle of real-time price execution and immediate settlement. Here’s a breakdown of the main types:
Forex Spot Market
The foreign exchange (forex) spot market is the largest and most liquid market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $7.5 trillion (BIS, 2022). Traders buy and sell currency pairs like EUR/USD or USD/JPY at current exchange rates, typically settled within T+2 days.
- Common among banks, institutions, and retail traders
- Driven by macroeconomic data, central bank policies, and geopolitical news
Cryptocurrency Spot Market
In the crypto spot market, traders exchange digital assets such as Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Solana (SOL) instantly at live market prices. Unlike derivatives or leveraged products, spot crypto trading gives users direct ownership of the coins.
- Settlement is almost instant via blockchain
- Available 24/7 on centralized and decentralized exchanges
Commodity Spot Market
This market involves trading physical commodities like gold, silver, crude oil, and agricultural goods for immediate delivery. Prices reflect the current market value of the physical asset and are used as benchmarks in global trade.
- Popular in metals (e.g., XAU/USD), oil (WTI, Brent), and agricultural products
- Often used by producers, refiners, and hedgers
Equity Spot Market
The stock market is technically a spot market where shares of publicly listed companies (e.g., Apple, Microsoft) are bought and sold for immediate settlement, typically T+2.
- Regulated by exchanges like NYSE, NASDAQ, HKEX
- Used by both institutional and retail investors for long-term or intraday strategies
Spot Trading vs Margin Trading
Before diving into leveraged strategies, it’s important to understand how spot trading differs from margin trading. While spot trading involves buying or selling assets using your own capital, margin trading allows you to borrow funds to increase exposure, which also increases both potential returns and risks. Here’s a direct comparison:
| Category | Spot Trading | Margin Trading |
| Leverage | No leverage | Uses borrowed funds |
| Ownership | Trader owns the asset | Trader borrows assets to trade |
| Risk Level | Lower, limited to capital invested | Higher, losses can exceed capital |
| Overnight Fees | No overnight fees | Includes interest and rollover charges |
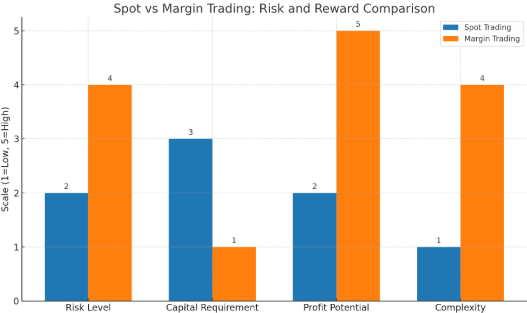
Spot Trading vs Futures Markets
Although both spot and futures markets allow traders to speculate on asset prices, their mechanics are fundamentally different. Spot trading involves immediate settlement at current market prices, whereas futures trading involves contracts with a set price and future delivery date. The table below highlights the key distinctions:
| Category | Spot | Futures |
| Settlement | Immediate or T+2 | On a future date |
| Pricing | Market-based (real-time) | Contractual price with expiry |
| Ownership | Direct asset ownership | Usually no (contract only) |
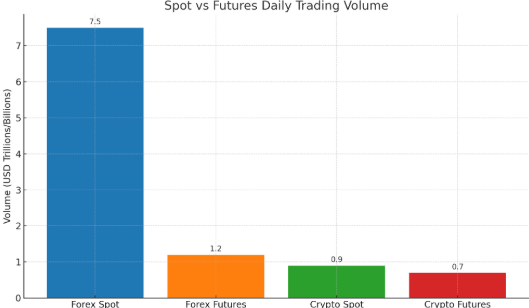
This bar chart compares the estimated daily trading volumes of spot and futures markets across forex and crypto sectors.
Key Highlights:
- Forex Spot dominates the global trading landscape with a daily volume of $7.5 trillion, making it the most liquid market in the world.
- Forex Futures comes next at $1.2 trillion/day, reflecting strong institutional participation.
- In the crypto market, spot trading volumes are around $0.9 billion/day, slightly higher than crypto futures at $0.7 billion/day.
- Spot markets—especially in forex—are significantly larger than their futures counterparts, highlighting their importance for real-time price discovery and immediate settlement.
What This Means for Traders:
- Spot markets are ideal for traders seeking direct ownership, lower risk, and greater liquidity.
- Futures markets are more suitable for hedging, leverage, and speculation, particularly among institutional players.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spot Trading
Spot trading is widely used for its simplicity and transparency, but like any trading method, it has both strengths and limitations. Understanding these pros and cons can help traders choose the right approach based on their goals and risk tolerance.
For example, spot traders benefit from no overnight fees, since positions aren’t leveraged. However, they also need to commit 100% of capital upfront, which can limit flexibility.
Advantages:
- Simple to understand: No derivatives or contracts involved.
- Lower costs: No hidden fees or interest payments.
- Real asset ownership: Suitable for long-term investors.
- Instant execution: Best for capitalizing on current price moves.
Disadvantages:
- No leverage: Limits potential returns.
- Market volatility: Spot prices can move sharply in response to news.
- Capital-intensive: Requires full amount to buy the asset.
Understanding these pros and cons helps traders align their strategies with their risk profile.
Spot Trading Strategies
Spot traders can adopt various strategies based on market conditions and timeframes:
- Trend Trading: Following the direction of the market using moving averages or trendlines.
- Range Trading: Buying low and selling high within a sideways range.
- Breakout Trading: Entering trades when price breaks through key support or resistance.
- News Trading: Reacting to economic releases or geopolitical events.
- Scalping: Taking small profits on short-term price movements, ideal in highly liquid markets.
These strategies can be adapted to different spot markets (forex, crypto, commodities) and should always be used with sound risk management, including stop-loss and position sizing.
Spot Trading Strategies Comparison Table
| Strategy | Description | Best For | Key Tools & Indicators |
| Trend Trading | Follows the market’s overall direction using trendlines and indicators. | Medium- to long-term traders | Moving Averages, MACD, RSI, ADX |
| Range Trading | Buys at support and sells at resistance in a sideways market. | Stable, non-trending markets | Bollinger Bands, RSI, Support/Resistance |
| Breakout Trading | Enters trades when price breaks key levels, anticipating strong movement. | Volatile or pre-news conditions | Volume Indicators, Breakout Patterns |
| News Trading | Reacts to economic or geopolitical news that causes sudden price moves. | Fast, experienced traders | Economic Calendar, Risk Management Tools |
| Scalping | Executes many trades to profit from small price changes throughout the day. | Active, high-frequency traders | 1–5 Min Charts, Level 2 Data, Tight Spreads |
Conclusion
Spot trading remains one of the most accessible, transparent, and low-risk ways to participate in financial markets. Whether in forex, crypto, or commodities, understanding what is spot trading and how it works is essential for any serious trader.
By avoiding leverage and focusing on real-time pricing, spot trading appeals to both beginner traders and long-term investors looking to build a stable portfolio.
Start exploring spot trading today with a trust broker like Ultima Markets and trade with confidence backed by institutional-grade tools and transparent pricing.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












