
Ultima Markets App
Trade Anytime, Anywhere
Important Information
This website is managed by Ultima Markets’ international entities, and it’s important to emphasise that they are not subject to regulation by the FCA in the UK. Therefore, you must understand that you will not have the FCA’s protection when investing through this website – for example:
- You will not be guaranteed Negative Balance Protection
- You will not be protected by FCA’s leverage restrictions
- You will not have the right to settle disputes via the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
- You will not be protected by Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- Any monies deposited will not be afforded the protection required under the FCA Client Assets Sourcebook. The level of protection for your funds will be determined by the regulations of the relevant local regulator.
Note: Ultima Markets is currently developing a dedicated website for UK clients and expects to onboard UK clients under FCA regulations in 2026.
If you would like to proceed and visit this website, you acknowledge and confirm the following:
- 1.The website is owned by Ultima Markets’ international entities and not by Ultima Markets UK Ltd, which is regulated by the FCA.
- 2.Ultima Markets Limited, or any of the Ultima Markets international entities, are neither based in the UK nor licensed by the FCA.
- 3.You are accessing the website at your own initiative and have not been solicited by Ultima Markets Limited in any way.
- 4.Investing through this website does not grant you the protections provided by the FCA.
- 5.Should you choose to invest through this website or with any of the international Ultima Markets entities, you will be subject to the rules and regulations of the relevant international regulatory authorities, not the FCA.
Ultima Markets wants to make it clear that we are duly licensed and authorised to offer the services and financial derivative products listed on our website. Individuals accessing this website and registering a trading account do so entirely of their own volition and without prior solicitation.
By confirming your decision to proceed with entering the website, you hereby affirm that this decision was solely initiated by you, and no solicitation has been made by any Ultima Markets entity.
I confirm my intention to proceed and enter this website Please direct me to the website operated by Ultima Markets , regulated by the FCA in the United KingdomWhat is the supply and demand curve: Understand price dynamics
Have you ever wondered why older Apple products drop in price after a new launch, why housing prices fluctuate, or why Uber uses dynamic pricing? The answer lies in the invisible curve that governs market economies—the supply and demand curve.
To understand how market prices change and lay the foundation for trading, it’s essential to first grasp the concept of the supply and demand curve.
This article will explore what the supply and demand curve is, the factors that influence it, and how to use it to improve your investment returns.
What Is the Supply and Demand Curve
The supply and demand curve is an economic graph that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good or service and its supply and demand. It consists of a supply curve and a demand curve.
What Is a Market
To understand the supply and demand curve, you first need to know what a market is.
Originally, a market was a physical location where buyers and sellers traded goods—such as a bazaar or shopping mall. Today, it can also be a digital platform like Amazon or Taobao.
Economist Gregory Mankiw defines a market as a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service. Buyers as a group determine the demand for a product, while sellers as a group determine the supply.

Demand Curve: Expression of Consumer Behavior
The demand curve connects price and quantity demanded. It represents the relationship between price and demand.
The quantity demanded of a good refers to the amount that buyers are both willing and able to purchase at a specific price.
Factors Influencing the Demand Curve:
- Income: An increase in income generally raises demand for most goods (normal goods), but reduces demand for inferior goods.
- Prices of related goods: A rise in the price of substitutes increases demand; a rise in the price of complements decreases demand.
- Consumer preferences: Changes in consumer tastes can affect demand.
- Expectations: Anticipation of future price increases can raise current demand.
- Population: A larger population increases total demand for a good.
Example: In the Hong Kong stock market, when a blue-chip stock announces a special dividend, investors expect higher returns, shifting the demand curve upward and driving the stock price up in the short term.
Supply Curve: Reflection of Producer Decision-Making
The supply curve shows the relationship between price and quantity supplied. It indicates the amount that sellers are willing and able to offer for sale at a specific price.
Factors Influencing the Supply Curve:
- Input prices: Inputs are resources used in production, such as raw materials, labor, and energy.
- Prices of related goods or services: Changes in prices of substitutes or complements can affect supply.
- Technology: Technological advances usually boost production efficiency and reduce costs, thereby increasing supply.
- Expectations: Producers’ expectations about future prices can influence current supply.
- Policy: Government policies, including taxes, subsidies, and regulations, also impact supply.
Example: When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, the cost of financing increases, leading to reduced bond issuance by companies listed in Hong Kong.
Market Equilibrium: The Dynamic Balance of the Supply and Demand Curve
When the demand curve and supply curve intersect on a graph, the point of intersection is called the market equilibrium. At this point, the quantity consumers are willing to buy exactly matches the quantity producers are willing to sell, creating a stable state regulated by market forces.
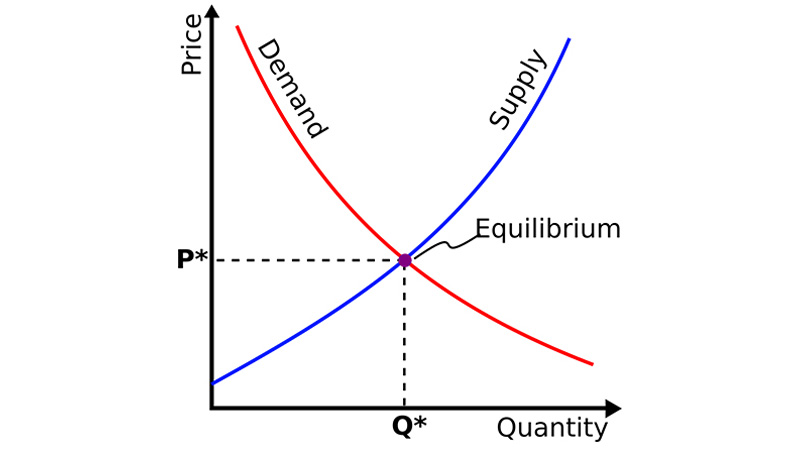
This stable condition is sometimes referred to as the market-clearing price, where the number of goods buyers are willing and able to purchase equals the number sellers are willing and able to offer. At this point, every buyer willing to pay the price can find a seller, and vice versa.
How to Use the Supply and Demand Curve to Determine Entry and Exit Points
When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise; conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices typically fall.
The supply and demand curve helps traders identify key support and resistance zones across different price levels, allowing them to anticipate future market trends.
By analyzing changes in supply (selling pressure) and demand (buying interest), investors can better time their trades and reduce overall risk.
Supply and demand curves are often visualized through charts showing volume density across price levels. A price zone with a concentration of unfilled buy orders is labeled a “demand zone” and may serve as future support. Conversely, zones with heavy sell order accumulation are known as “supply zones” and may act as resistance.
Common Strategies for Timing Trades:
- Buy at Demand Zone: When price approaches a historical demand zone and shows signs of reversal, it may signal a good buying opportunity.
- Sell at Supply Zone: When price nears a supply zone and momentum weakens, it’s often a good time to take profits or enter a short position.
- Breakout & Retest: If price breaks through a key supply or demand zone and successfully retests it, this often indicates a continuation of the trend, making it suitable for trend-following strategies.
With supply and demand indicators, traders can visualize market structure and pre-plan entry and exit points to improve success rates. When combined with other technical tools like RSI or MACD, the strategy becomes even more robust and reliable.
For beginner traders, it is recommended to start with a demo account to practice trading in a simulated environment. This helps them get familiar with market volatility and fee structures while minimizing real capital risks. You can also visit the Ultima Markets homepage to learn more about the market and access investment tutorials.

FAQ
Q: How can I use the supply and demand curve to formulate a buy-the-dip strategy?
A: The key lies in identifying a genuine demand zone. Look for a sudden spike in volume after a period of low activity, which may indicate selling pressure exhaustion or active accumulation by buyers. To confirm the support’s validity, watch for bullish candles engulfing previous lows as a sign of a reversal.
Q: Why does the price often reverse or rebound at specific levels?
A: This is usually due to hidden demand or supply zones at work. These are areas where high-volume transactions occurred previously—indicating a buildup of either buy (demand zone) or sell (supply zone) orders. These levels become battlegrounds for bulls and bears. On Ultima Markets, you can use advanced tools to easily identify these key supply and demand zones.
Q: Why is a breakout above a supply zone considered a strong signal in futures trading?
A: A supply zone often contains a large number of trapped sell orders. If price breaks above this zone with strong volume, it signals that buying demand is powerful enough to absorb selling pressure—indicating the demand curve is now dominating the market. At this point, the supply zone flips from resistance to support, often accompanied by a trend continuation. Traders can ride the breakout by entering long positions and setting a stop loss just below the breakout level.
Conclusion
The financial markets are captivating because they are constantly evolving, filled with new variables and challenges.
But no matter how the markets shift, the supply and demand curve always reveals a fundamental truth: the ultimate direction of price lies in the dynamic balance between buying and selling forces. When you begin to view the market through the lens of supply and demand, you move beyond mere price-chasing and step into a higher dimension of investing—one where you can truly interpret market structure and master trend movements.
Log in to the Ultima Markets trading platform now to access real-time market data and begin your trading journey—the starting point for your next precise decision may be hidden in the very first trendline you draw.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute, and should not be construed as, financial, investment, or other professional advice. No statement or opinion contained here in should be considered a recommendation by Ultima Markets or the author regarding any specific investment product, strategy, or transaction. Readers are advised not to rely solely on this material when making investment decisions and should seek independent advice where appropriate.












