What Is the VIX Volatility Index and How Does It Work
In today’s highly volatile global financial markets, understanding shifts in investor sentiment has become an essential task for every trader. The VIX Volatility Index is a crucial tool used to gauge fear in the market and to anticipate potential price fluctuations. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a beginner just starting to explore investing, grasping how the VIX functions will help you better navigate market turbulence. This article offers a comprehensive, professional breakdown of the VIX Index’s definition, calculation method, practical trading applications, and risk management techniques.
What Is the VIX Index? A Professional Breakdown of the “Fear Gauge”
The VIX Volatility Index, launched in 1993 by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), measures the implied volatility of S&P 500 Index options and expresses the market’s expected volatility over the next 30 days in percentage terms. When uncertainty rises or fear spreads across the market, the VIX typically spikes—earning it the nickname “fear gauge.”
Simply put, a rising VIX indicates that market participants expect increased volatility ahead, while a declining VIX suggests more stability and improving risk appetite. By monitoring movements in the VIX Index, investors can anticipate shifts in equity trends and price volatility across asset classes.

How the VIX Is Calculated: Reading Sentiment from the Options Market
The VIX is calculated using a complex weighted average formula based on prices of S&P 500 call and put options across various strike prices and expiration dates. The core logic of the calculation involves:
- Selecting a range of options with different expiration dates and strike prices
- Applying a weighted average to their implied volatilities
- Annualizing the result and expressing it as a percentage
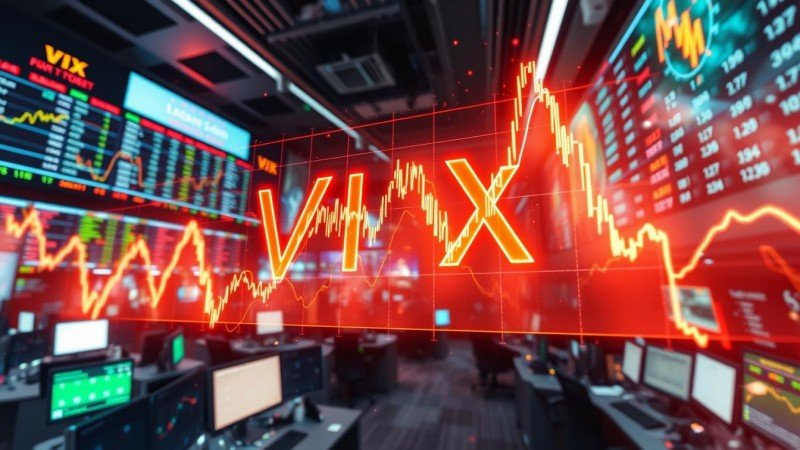
A higher VIX indicates a stronger market expectation of future volatility, while a lower VIX reflects expectations of relative calm. Because it is derived from actual market pricing, the VIX provides a highly responsive and real-time barometer of investor sentiment.
How to Interpret the VIX Index? Value Breakdown and Market Implications
The VIX Volatility Index can be interpreted using a general range-based approach, as shown below:
| VIX Value Range | Market Sentiment | Implication |
| 0–20 | Stable or Optimistic | Low expected volatility, strong risk appetite |
| 20–30 | Mildly Nervous | Rising uncertainty in the market |
| 30–50 | High Panic | Anticipation of sharp market swings, shift to safe-haven assets |
| 50+ | Extreme Fear | Typically linked to systemic risk events |
Understanding these value ranges allows investors to formulate responsive strategies across different market cycles—such as adjusting leverage levels, initiating hedging positions, or timing entry points.
VIX and the S&P 500: Understanding Their Inverse Correlation
Historical data shows that the VIX Index tends to move inversely with the S&P 500 Index. When equity markets decline and risk-off sentiment intensifies, investors often seek protection by purchasing S&P 500 options, driving up implied volatility and pushing the VIX higher. Conversely, during equity rallies, the VIX typically retreats.
This negative correlation makes the VIX a valuable indicator for tracking shifts in hedging demand and offers investors an opportunity to identify potential market inflection points based on volatility trends.
VIX Investment Methods: Strategies for Multi-Scenario Applications
- VIX Futures Contracts: Trade the expected future value of VIX directly—suitable for short-term hedging strategies.
- VIX ETFs/ETNs: Instruments like VXX and UVXY replicate VIX futures exposure, offering retail investors an accessible entry point.
- CFD Trading: On platforms such as Ultima Markets, investors can open a trading account to apply flexible leverage on VIX-linked products.
- Options Strategies: Implement advanced volatility trades such as straddles and strangles to capture price swings.
Each tool carries different characteristics in terms of leverage, liquidity, and cost structure. Traders should select based on their capital size, risk tolerance, and trading habits.
VIX and Market Sentiment: A Direct Reflection of Investor Psychology
The VIX is widely followed because it vividly reflects the collective emotional state of the market. Poor economic data, geopolitical instability, or unexpected “black swan” events tend to trigger sharp spikes in the VIX.
Monitoring short-term VIX surges or prolonged lows helps anticipate potential turning points in the market. It also aids in adjusting asset allocation—for instance, increasing exposure to gold and commodities or reducing holdings in high-volatility equities.
VIX and Hedging Tactics: Managing Portfolio Risk with Precision
In practice, the VIX can guide investors in constructing dynamic hedging positions:
During High VIX Phases: Reduce equity exposure and allocate more to cash, gold, or volatility-based products.
During Low VIX Phases: Increase allocation to equities and risk assets such as bonds to capitalize on growth opportunities.
On the Ultima Markets platform, traders can first use a demo account to backtest strategies across different volatility scenarios. Once familiar with market behavior, they can transition to live execution via a trading account.

Frequently Asked Questions About VIX Investing
Q1: Is the VIX always inversely correlated with the stock market?
A: Most of the time, yes. VIX typically moves in the opposite direction of the equity market. However, during extreme liquidity crises—such as the 2008 financial meltdown—both the VIX and stock indices may rise simultaneously.
Q2: Can I trade the VIX Index directly?
A: No. The VIX spot index itself is not directly tradable. Participation is only possible via derivative instruments such as futures, ETFs, and CFDs.
Q3: Does a rising VIX mean the stock market will crash?
A: Not necessarily. A rising VIX generally signals growing market anxiety, but it does not automatically predict a market crash. Other macroeconomic indicators and structural signals must be considered.
Q4: What kind of investor is VIX trading suitable for?
A: VIX-linked products are more appropriate for intermediate to advanced investors who understand futures or leveraged instruments and seek flexible hedging strategies.
Q5: How can beginners start exploring VIX-related trading?
A: Beginners are advised to start with VIX ETFs or open a demo account on the Ultima Markets platform to practice trading in volatile conditions.
Conclusion: The VIX Is a Compass in Volatile Markets
The VIX Volatility Index serves as a vital heartbeat monitor for global markets. Understanding its movements enables investors to anticipate risk shifts early. Whether for hedging, capturing short-term opportunities, or optimizing portfolio allocation, mastering the VIX is an essential skill for navigating market turbulence.






![[MetaTrader 5 Mobile Trading Complete Guide] 7 Key Advantages for Real-Time Market Access](https://www.ultimamarkets.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/mt5_mobile_trading_card.jpg)