Comprehensive Guide to Forex Trading for Beginners: From Basics to Platform Selection, Easily Step into the Forex Market
Forex trading is a global investment method that has attracted countless investors due to its high liquidity and 24-hour trading availability. For beginners, entering this market might seem challenging, as forex trading involves numerous professional terms, complex market analysis methods, and various trading strategies. However, by mastering the basic concepts and adopting the right learning approach, forex trading can also bring you stable returns.
This article will start with the fundamentals, helping you gain a deeper understanding of how the forex market operates, common currency pairs, core trading terminology, and how to choose the best trading opportunities. We will also introduce the advantages and risks of forex investment, analyze common trading strategies, and provide advice on selecting the right platform, enabling you to continuously improve your trading skills through practice.
Whether you are a complete novice or already have some basic knowledge, this article will serve as the best starting point for entering the forex market. Let’s step into this opportunity-filled market together, gradually master the essence of forex trading, and lay a solid foundation for your investment journey!
What is Forex Trading: Understanding the Concept
Forex trading (Foreign Exchange) is one of the most active trading methods in the global financial market, referring to the process of exchanging currencies from different countries. Whether it’s for currency exchange due to travel needs or for investing by leveraging currency price fluctuations, the forex market offers high flexibility and convenience, attracting an increasing number of investors. As people seek diversified ways to grow their assets, forex trading has gradually become a popular financial tool for many.
For example, suppose Investor B purchases the equivalent amount of Japanese yen with 5,000 British pounds. A few days later, due to changes in the exchange rate between the yen and the pound, they sell the yen they hold and ultimately exchange it back for 5,300 British pounds, thereby earning a profit of 300 pounds from the price difference. This is the core operation of forex trading: earning profits through buying and selling currencies.
It’s important to note that currency values fluctuate based on market conditions, economic indicators, and political events. Therefore, investors are essentially predicting and trading the “future value” of currencies. In other words, exchange rate movements in the forex market are highly unpredictable, and investors cannot precisely forecast future trends. They can only make the best judgments and choices based on current market conditions. Because of this, forex trading also carries certain risks, which every investor must carefully consider when engaging in forex trading.
Understanding the basic principles and operational mechanisms of the forex market, and learning how to make reasonable judgments based on market dynamics, will help you achieve success in forex trading.
Core Elements of Forex Trading: Advanced Understanding
The core of forex trading revolves around the exchange between two currencies, and its essence involves the following key elements:
- Currency Pair
Every transaction in the forex market involves a combination of two currencies, known as a currency pair. For example, the Euro/US Dollar (EUR/USD) and the US Dollar/Japanese Yen (USD/JPY) are common currency pairs. A currency pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency. Investors need to analyze the price trends of these currency pairs to predict future exchange rate movements and develop trading strategies accordingly.

Base Currency
EUR (Euro) 🇪🇺
Quote Currency
USD (US Dollar) 🇺🇸
- Exchange Rate
The exchange rate is the price at which one currency can be exchanged for another, and it fluctuates based on market supply and demand. Numerous factors influence exchange rate movements, including economic data (such as GDP growth rates, employment reports), central bank interest rate policies, and international political and geopolitical conflicts. Continuously tracking these changes is part of the daily routine for forex traders. - Trading Actions
Forex trading operations, in simple terms, involve “buying low and selling high” or “selling high and buying low.” Investors, based on their market trend predictions, choose to buy (going long) or sell (going short) specific currency pairs to capitalize on potential gains from exchange rate fluctuations. For example, when predicting that the US dollar will appreciate, an investor might choose to buy the USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen) pair, aiming to profit from the rising exchange rate.
Basic Components of Forex Trading: The First Step to Understanding Forex
| Component | Definition | Characteristics | Example |
| Base Currency | The first currency in a currency pair, located on the left side of the quote, always valued at “1”. | – All transactions revolve around the base currency. – Buying a currency pair means buying the base currency and selling the quote currency. |
In the EUR/USD quote of 1.1918, the base currency is the Euro, meaning 1 Euro equals 1.1918 US Dollars. |
| Quote Currency | The second currency in a currency pair, located on the right side of the quote, representing the amount needed to exchange 1 unit of the base currency. | – The price of the quote currency fluctuates with market changes. – Profits and losses are calculated in the quote currency, reflecting the market value of the base currency. |
In the GBP/USD quote of 1.3850, the US Dollar is the quote currency, meaning 1.3850 US Dollars are needed to exchange for 1 British Pound. |
| Bid Price | The price at which traders are willing to sell the base currency, usually displayed on the left side of the quote and often marked in red. | – Reflects market demand for the base currency. – The bid price updates in real-time based on market supply and demand. |
In the quote 1.1916/1.1918, 1.1916 is the bid price, meaning 1 Euro can be sold for 1.1916 US Dollars. |
| Ask Price | The price at which traders are willing to buy the base currency, usually displayed on the right side of the quote and often marked in blue. | – The ask price is typically higher than the bid price, with the difference being the transaction cost (spread). – The ask price fluctuates with market activity. |
In the quote 1.1916/1.1918, 1.1918 is the ask price, meaning 1.1918 US Dollars are needed to buy 1 Euro. |
Popular Forex Currency Pairs: Essential Knowledge for Beginners
In the forex trading market, choosing the right currency pair is a crucial step for beginner investors entering the market. A currency pair is the basic unit of forex trading, consisting of two currencies that reflect their exchange rate relationship. Below is a list of the most popular currency pairs in global forex trading. These pairs not only have high trading volumes and strong liquidity but also help beginners quickly understand market dynamics:
| Currency Pair | Percentage of Global Trading Volume | Characteristics and Importance |
| EUR/USD | ~30% | As the most traded currency pair in forex, EUR/USD offers extremely high liquidity and stable volatility. It is influenced by economic data from Europe and the US, making it the best choice for beginners. |
| USD/JPY | ~13.5% | The Japanese Yen is considered a safe-haven currency. USD/JPY volatility is driven by market risk sentiment and Japanese economic policies, making it suitable for beginners looking to understand exchange rate fluctuations. |
| GBP/USD | ~12% | The combination of the British Pound and the US Dollar is influenced by UK economic data and the US Dollar Index. It has relatively large volatility, making it suitable for investors with some forex trading experience. |
| AUD/USD | ~5.4% | The Australian Dollar is a commodity currency, with its exchange rate influenced by commodity prices (such as iron ore) and Chinese economic demand. Its relatively stable volatility makes it a good choice for beginners to further learn market analysis. |
| USD/CAD | ~5% | The Canadian Dollar is considered an oil-related currency. The USD/CAD exchange rate is closely tied to international oil prices, making it suitable for investors studying the energy market and forex trading. |
| USD/CHF | ~3.5% | The Swiss Franc is a safe-haven currency. USD/CHF trading volume increases during global market turmoil, making it suitable for beginners interested in studying safe-haven strategies. |
| USD/CNY | ~3% | With the rise of China’s economy, the trading volume of USD/CNY has been increasing year by year. Its exchange rate is influenced by Chinese economic policies and global trade changes, making it a focus in emerging markets. |
How Beginners Can Choose Forex Currency Pairs?
In forex trading, beginners often choose currency pairs with the highest liquidity and greater transparency of information as their starting point. Here are some key points to consider when selecting currency pairs:
- High Liquidity: Popular currency pairs (such as EUR/USD and USD/JPY) have strong liquidity and lower transaction costs, making them suitable for frequent buying and selling operations.
- Abundant Information Sources: Market analysis and economic data for popular currency pairs are easily accessible, helping beginners quickly grasp the basic skills of forex trading.
- Moderate Volatility: For beginners, currency pairs with moderate volatility (such as EUR/USD and AUD/USD) can effectively reduce trading risks.
Learning Recommendations for Forex Currency Pairs
- EUR/USD as the First Choice: This is the most traded and stable currency pair in the forex market. Beginners can use it to learn basic market operations and understand the impact of economic data on exchange rates.
- Gradually Explore Other Currency Pairs: After mastering the basics, beginners can try currency pairs with higher volatility (such as GBP/USD or USD/JPY) to enhance their analytical and response capabilities.
Detailed Classification of Forex Currency Pairs: A Must-Read Guide for Beginners
In forex trading, understanding the classification of currency pairs is essential foundational knowledge for novice traders. Different types of currency pairs have distinct characteristics and trading strategies, which directly impact investors’ risks and returns. Below, we will explore the definitions and features of major currency pairs, cross currency pairs, and exotic currency pairs to help you better choose the trading combinations that suit you.
| Category | Definition | Characteristics | Common Currency Pairs |
| Major Currency Pairs | Major currency pairs are the most traded and highly liquid currency combinations in the forex market, always including the US Dollar (USD) and currencies of other major global economies. These pairs account for over 80% of global forex trading volume and are the core of the market. | – **High Liquidity**: Many market participants, quick buying and selling, easy to execute trades. – **Low Spreads**: Lower costs due to high trading volume, suitable for beginners. – **High Stability**: Associated with economically stable countries, less volatility. – **High Market Transparency**: Driven by global economic data, policies, and market trends, with transparent and easily accessible information. |
– EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) – GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar) – USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen) – USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc) – AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar) – USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar) – NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar/US Dollar) |
| Cross Currency Pairs | Cross currency pairs do not include the US Dollar, meaning the two currencies can be exchanged directly without converting through the USD. These pairs often involve major currencies like the Euro (EUR), British Pound (GBP), or Japanese Yen (JPY). | – **Moderate Liquidity**: Although not as high as major currency pairs, some popular cross pairs still have strong liquidity. – **Higher Volatility**: More influenced by regional economic and political factors due to the absence of the USD. – **Arbitrage Opportunities**: Investors can exploit interest rate differences between currencies. – **Suitable for Intermediate Traders**: Requires a good understanding of the currency pairs and their related economies to better predict market trends. |
– EUR/GBP (Euro/British Pound) – EUR/CHF (Euro/Swiss Franc) – EUR/JPY (Euro/Japanese Yen) – GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen) – AUD/JPY (Australian Dollar/Japanese Yen) |
| Exotic Currency Pairs | Exotic currency pairs consist of currencies from emerging markets or developing countries paired with major currencies (such as USD or EUR). These pairs have lower liquidity and fewer market participants. | – **Low Liquidity**: Smaller trading volumes may result in larger spreads. – **High Volatility**: Prone to sharp price fluctuations due to political instability, economic uncertainty, and sudden events. – **High Risk and Reward**: While risky, they can offer high returns during significant volatility. – **Strongly Influenced by Economic Factors**: Exchange rates are directly affected by inflation, international debt, and interest rate changes. |
– USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira) – USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South African Rand) – USD/BRL (US Dollar/Brazilian Real) – USD/MXN (US Dollar/Mexican Peso) – USD/INR (US Dollar/Indian Rupee) |
The Concept of “Pip” in Forex Trading: Basics and Importance
In forex trading, the “pip” (Percentage in Point) is an essential core concept, representing the smallest unit of price movement in the forex market. For beginner investors, understanding the definition of a pip, how to calculate it, and its application in trading is crucial for accurately assessing market trends and developing trading strategies.
What is a Pip?
A pip is the basic unit of price movement in currency pairs. Typically:
- For **most currency pairs**, prices are quoted to the fourth decimal place (e.g., EUR/USD: 1.1050). The smallest price movement is 0.0001, which equals **1 pip**.
- For Yen-related currency pairs(e.g., USD/JPY), prices are quoted to the second decimal place (e.g., USD/JPY: 110.25). The smallest price movement is 0.01, also referred to as **1 pip**.
Examples:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar): If the price moves from 1.1200 to 1.1205, it has increased by 5 pips(0.0005).
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen): If the price drops from 135.60 to 135.50, it has decreased by 10 pips(0.10).
These small price movements directly impact profit or loss calculations in forex trading, making it essential to understand the concept of pips.
Importance of Pips: Core Applications in Forex Trading
- Measuring Price Movements:
- Pips serve as the smallest unit for measuring price changes, allowing investors to analyze market trends precisely.
- Example: If EUR/USD moves from 1.1000 to 1.1020, it has risen by **20 pips**. For a standard lot (100,000 units of the base currency), this could result in a $200 profit or loss.
- Calculating Trading Costs:
- The spreadin forex trading refers to the difference between the bid and ask prices, usually measured in pips.
- A smaller spread means lower trading costs. For example, EUR/USD might have a spread of 1 pip, while more volatile pairs like GBP/NZD could have spreads as high as 5 pips.
- Assessing Potential Profits and Risks:
- Forex trading is conducted in “lots,” where 1 standard lot equals 100,000 units of the base currency. Even a 1-pip movement can result in significant profits or losses in large trades.
- Example: In a 1-lot USD/JPY trade, a 1-pip movement equals 1,000 JPY (approximately $10). A 50-pip movement could result in a $500 profit or loss.
- Impact in High-Volume Markets:
- The forex market is the largest financial market globally, with a daily trading volume exceeding $7 trillion. Even a few pips of price movement can significantly impact traders’ overall profits or losses.
Learning Tips for Forex Beginners:
- Focus on Popular Currency Pairs: Such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY, which have low spreads and stable volatility, making them ideal for beginners to learn about pips.
- Practice Calculating Pip Gains or Losses: Use demo accounts on trading platforms to simulate trades and understand the role of pips in real trading scenarios.
- Understand Risk Management: Learn to set stop-loss and take-profit levels to control the range of pip movements in each trade, minimizing potential losses.
Spread and Pip Value in Forex Trading: Core Concepts for Beginners
In forex trading, spread and pip value are two critical concepts that directly impact trading costs and how market movements are measured. For beginner investors, understanding these concepts is essential for developing effective trading strategies.
- Spread: Measuring Trading Costs
In the forex market, every currency pair has two prices: the Ask price (buy price) and the Bid price (sell price). The difference between these two prices is known as the **spread**.
– What is Spread?
The spread represents the cost you pay to enter the market. It is the hurdle you must overcome before you can start making a profit.
– How to Calculate Spread:
For example, if the AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar) has an Ask price of 0.7550 and a Bid price of 0.7547, the spread is **0.0003**, or **3 pips**.
– Impact of Spread on Trading:
– A smaller spread means lower trading costs, which is favorable for investors.
– A larger spread increases trading costs, meaning you need a larger price movement to achieve profitability.
– Example:
If you go long (buy) on AUD/USD, you will only start making a profit if the market price rises above the spread you paid. Similarly, when going **short**, the market price must fall below the Bid price minus the spread to realize a profit.
- Pip Value: The Basic Unit of Price Movement
In forex trading, pip value is the smallest unit used to measure price movements. Each currency pair’s price fluctuations are calculated in pips, allowing investors to accurately assess the potential impact of market changes.
– Definition of Pip Value:
– For **most currency pairs**, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) and GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar), 1 pip represents a movement at the fourth decimal place, or **0.0001**.
– For **Yen-based currency pairs**, such as USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen), 1 pip represents a movement at the second decimal place, or **0.01**.
– Examples:
– If USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar) moves from 1.3421 to 1.3423, it has increased by 2 pips (0.0002).
– If USD/JPY moves from 110.30 to 110.32, it has also increased by 2 pips (0.02).
– Importance of Pip Value:
Pip value helps you understand the specific impact of market movements on your trades. For example, if you trade 1 standard lot of EUR/USD, each pip movement is worth approximately **$10**. This means that for every 1-pip change in price, you could gain or lose $10.
Summary: How to Use Spread and Pip Value to Develop Trading Strategies
– Spread is the cost of entering the market. Choosing currency pairs with smaller spreads, such as EUR/USD or **USD/JPY**, can help reduce trading costs and is ideal for beginner traders.
– Pip value helps you measure the impact of market movements on profits and risks. Understanding pip value allows you to calculate potential gains and losses more accurately.
By mastering the concepts of spread and pip value, you can better calculate trading costs, predict market trends, and develop more effective forex trading strategies to achieve steady profits.
Positions in Forex Trading: Essential Knowledge for Beginners
In forex trading, a position refers to an open trade that a trader holds in the market. In simple terms, it means that your trade is active and has not yet been closed. The performance of a position is closely tied to market price movements, and the profit or loss of an investor depends on the accuracy of their market predictions. For beginners in forex trading, understanding the concept of positions is crucial for effective risk management and profit strategies.
Based on market expectations, positions in forex trading can be divided into two main types: long positions and **short positions**.
-
Long Position: A Strategy for Bullish Markets
- Definition: A long position is when a trader buys a currency pair, expecting its price to rise, with the intention of selling it at a higher price in the future to profit from the price difference.
- Operation Logic:
- When you predict that a currency will appreciate, you can open a long position. In simple terms, you buy the currency and sell it later at a higher price.
- Example:
- Suppose you expect the USD/CADexchange rate to rise, and the current price is 1.2700. You buy 1 lot of USD/CAD at this price, establishing a long position. If the exchange rate rises to 1.2750 a few days later, you can sell it, earning a profit of **50 pips**. At this point, your long position is closed, and the trade is completed, resulting in a profit.
- Key Points of Long Positions:
- Suitable for situations where you predict the market will rise.
- If the buying price is lower than the selling price, you can earn a profit from the price difference.
-
Short Position: A Strategy for Bearish Markets
- Definition: A short position is when a trader sells a currency pair, expecting its price to fall, with the intention of buying it back at a lower price in the future to profit from the price difference.
- Operation Logic:
- When you believe a currency will depreciate, you can open a short position. This means you sell the currency first and buy it back later at a lower price to earn a profit.
- Example:
- Suppose you believe the GBP/USDexchange rate will fall, and the current price is 1.3300. You sell 1 lot of GBP/USD, establishing a short position. If the exchange rate drops to 1.3250 a few days later, you can buy it back at this lower price, earning a profit of **50 pips**. At this point, your short position is closed, and the trade is completed, resulting in a profit.
- Key Points of Short Positions:
- Suitable for situations where you predict the market will fall.
- If the selling price is higher than the buying price, you can profit from the price decline.
Importance of Positions: The Key to Profit and Risk
- Market Direction Judgment:
- The establishment of a position reflects your prediction of market trends.
- If you predict the market will rise, you should open a **long position**.
- If you predict the market will fall, you should open a **short position**.
- Source of Profit and Loss:
- Your trading profit or loss comes from the price movements of the currency pair. If the market moves in line with your prediction, you will earn a profit; otherwise, you will face a loss. Therefore, accurately predicting market trends is crucial for achieving profits.
- Risk Management:
- Risk management is critical in forex trading, especially when positions are open. Market price fluctuations can impact your positions, so learning to set stop-lossand take-profit levels can help you control risks and achieve stable profits. For beginner investors, managing positions effectively can reduce losses and increase the probability of successful trades.
Summary: How to Manage Your Forex Positions
In forex trading, understanding how to operate long and short positions and developing strategies based on market predictions are essential for beginner investors. By mastering these basic concepts and techniques, you will be better equipped to seize opportunities in the market and manage risks effectively.
Practical Guide to Forex Trading: Types, Operations, and Strategies
Overview of Forex Trading Types
Choosing the right type of forex trading is crucial for every beginner investor entering the market. Different trading types have their own characteristics and suitable scenarios. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions. Below, we analyze the four main types of forex trading through a table to help you build a solid foundation in forex investment.
| Trading Type | Introduction | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable Scenarios |
| Spot Forex | Directly buying or selling foreign currency cash or deposits from banks. Simple and suitable for beginners. | – Easy to operate, no need to hold physical currency – Immediate settlement, fast transactions |
– Higher transaction costs – Limited trading hours, fewer currency pairs available |
Suitable for immediate transactions, such as forex travel or short-term investments. |
| Forward Forex | An agreement to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date, used by businesses to hedge against exchange rate risks. | – Locks in exchange rates, avoiding volatility risks – Suitable for large transactions and risk management |
– Fixed settlement dates, lack of flexibility – Mainly used by businesses, not suitable for small investors |
Suitable for planning future payments or income, such as import/export businesses needing to lock in exchange rates. |
| Forex Futures | Trading standardized forex contracts on futures exchanges, with settlement at a future date based on agreed rates. | – High liquidity, easy to trade – Standardized contracts with clear rules |
– Fixed settlement dates, no flexibility – High market volatility and risks |
Suitable for intermediate investors looking to hedge short-term price fluctuations, especially institutional investors. |
| Forex Margin Trading | Trading with leverage, allowing investors to control large positions with a small margin deposit. | – High leverage, amplifying profit potential – No need to hold physical currency, high capital efficiency |
– High risk, potential for amplified losses – Requires careful selection of trading platforms to avoid scams |
Suitable for short-term traders or investors with higher risk tolerance, especially those seeking quick profits. |
Detailed Analysis: Operation Methods and Application Scenarios of Each Trading Type
- Spot Forex TradingSpot forex is the simplest and most common form of forex trading, where you directly buy or sell foreign currency cash or deposits from banks. This type of transaction typically does not require waiting for settlement, and you can receive physical currency or transfer funds to a designated account immediately after the trade.
- Example: If you expect the US Dollar (USD) to appreciate, you can buy USD with Singapore Dollars (SGD). When the USD rises, you can sell it back for SGD, earning a profit from the exchange rate difference.
- Forward Forex TradingForward forex involves an agreement between two parties to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. This is commonly used by businesses for risk management, especially to hedge against future exchange rate fluctuations.
- Example: A company expecting to pay $1 million for raw materials in three months can sign a forward forex contract with a bank to lock in the future exchange rate.
- Forex Futures TradingForex futures involve trading standardized forex contracts on futures exchanges, with settlement at a future date based on agreed rates. The forex futures market is highly liquid but subject to significant price volatility, making it relatively risky.
- Example: If you expect the USD/JPY to appreciate, you can buy USD futures contracts and sell them later at a higher price to profit from the price difference.
- Forex Margin TradingForex margin trading allows you to use leverage to control larger positions with a small margin deposit. This type of trading is suitable for investors with limited capital but higher risk tolerance, especially short-term traders.
- Example: With a $200 margin and 1:200 leverage, you can control $40,000 in forex trading. If the market moves in your favor, you can achieve significant profits, but losses can also be amplified.
How to Operate Forex Trading?
After understanding the basics of the forex market, the next step is to master the practical methods of forex trading. This section will help you better grasp market trends and develop effective forex investment strategies from both fundamental and technical analysis perspectives.
📈 Fundamental Analysis: How to Uncover Trading Opportunities from Economics and Policies
Fundamental analysis focuses on macroeconomic factors and policy changes, serving as a key tool for judging medium- to long-term market trends. By analyzing global economic indicators and central bank policies, you can identify the fundamental drivers affecting the forex market.
- Central Bank Monetary PoliciesMonetary policy is one of the key drivers of the forex market. Central banks adjust interest rates, implement quantitative easing, or tighten policies to regulate money supply, thereby influencing exchange rate fluctuations.
- Example: If the European Central Bank raises interest rates, the Euro may appreciate due to increased attractiveness. Conversely, if the Bank of Japan implements more monetary easing, the Yen may depreciate.
- Impact:
- Rate Hikes: Typically strengthen the currency as higher interest rates attract more capital inflows.
- Rate Cuts: May weaken the currency as lower interest rates reduce investment returns.
- Interpreting Economic IndicatorsForex market fluctuations are closely tied to economic data. Understanding key economic indicators is crucial for forex trading.
- Policy Rates: Affect short-term exchange rates.
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product): A primary indicator of economic growth; strong GDP growth often supports currency demand.
- Unemployment Rate: Reflects economic health; low unemployment indicates economic prosperity.
- Trade Balance: A trade surplus benefits the domestic currency, while a trade deficit may weaken it.
- Example: If the UK reports stronger-than-expected GDP growth, the market may favor the British Pound (GBP) due to robust economic growth.
- Conclusion: By combining these fundamental factors, you can predict market trends, which is particularly important for medium- to long-term trading strategies.
📊 Technical Analysis: Capturing Trading Opportunities Through Data Charts
Technical analysis focuses on historical price movements, allowing investors to predict future market trends by analyzing price charts. The core idea is that all market information and sentiment are reflected in price movements.
- Trend Identification: Recognizing Peaks and TroughsThe foundation of technical analysis is identifying trends, particularly price peaks and troughs.
- Uptrend (Bullish Trend): When price peaks and troughs gradually rise, indicating a rising market suitable for buying.
- Downtrend (Bearish Trend): When price peaks and troughs gradually fall, indicating a declining market suitable for selling.
- Using Candlestick Charts: Capturing Market ReversalsCandlestick charts are the most commonly used tool in technical analysis, clearly reflecting price fluctuations. Each candlestick shows the open, close, high, and low prices, with colors distinguishing between gains and losses.
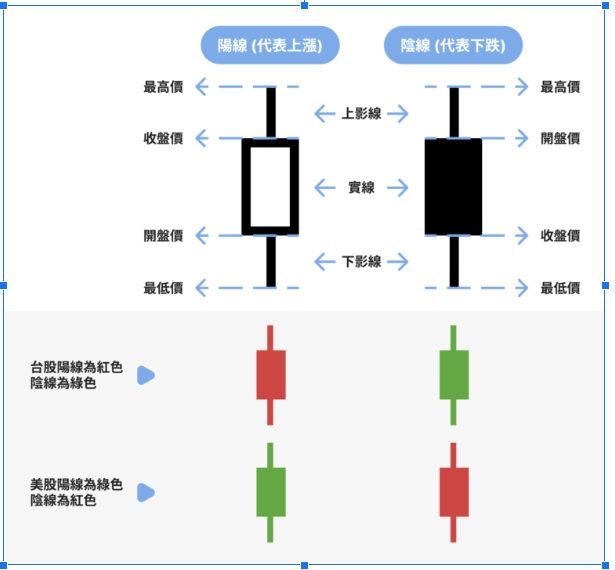
Bullish Candle (Rising Price): The closing price is higher than the opening price, indicating market strength, and is typically represented in green.
Bearish Candle (Falling Price): The closing price is lower than the opening price, indicating market weakness, and is typically represented in red.
Examples:
- If a series of consecutive bullish candles is observed, it may indicate a strong upward trend, suggesting a good opportunity to enter a buy position.
- If a head and shoulders pattern forms, it may signal a market reversal, suggesting a good opportunity to sell.
Conclusion: By comprehensively analyzing peaks, troughs, and candlestick patterns, investors can timely capture market turning points and execute precise operations.
3.Bar Charts: Understanding Price Ranges in Forex Trading
Bar charts are a tool similar to candlestick charts in function, but their data presentation is more intuitive. They are particularly helpful in displaying price ranges, opening prices, and closing prices, enabling forex traders to quickly interpret market trends.
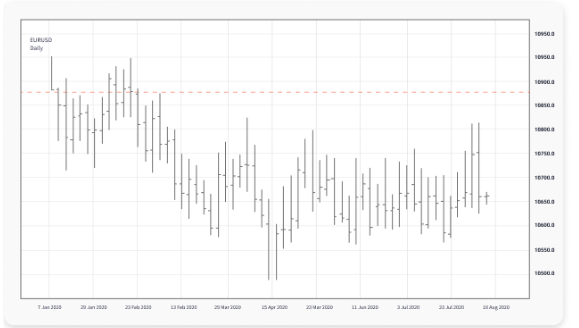
Analysis of Bar Chart Structure:
- Top and Bottom: Represent the highest and lowest prices during the trading period.
- Horizontal Lines:
- The horizontal line on the left sideof the bar indicates the **opening price**, which is the starting price of the period.
- The horizontal line on the right sideof the bar indicates the **closing price**, which is the ending price of the period.
Applicable Scenarios:
Bar charts are highly suitable for advanced forex trading analysis, especially for investors who want a comprehensive understanding of price volatility ranges. Compared to candlestick charts, bar charts have a simpler structure but are rich in information, making it easy to visually determine whether prices are in a volatile range or if there is a clear market breakout.
Example:
Suppose the Euro/US Dollar (EUR/USD) shows a long bar pattern on a trading day, with the closing price near the highest price. This usually indicates strong bullish momentum in the market, suggesting that the Euro may continue to strengthen. At this point, you can combine technical indicators to confirm entry timing and plan a follow-up long strategy.
4.Line Charts: A Beginner’s Tool for Forex Trading
For beginners in forex trading, line charts are an ideal choice for learning market trends. They present price movements in a simple and clear format, helping newcomers quickly grasp changes in the forex market.
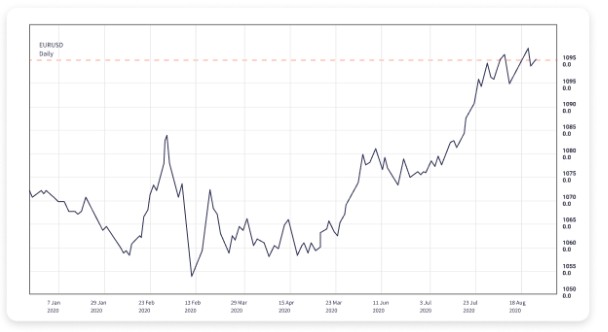
Structure and Characteristics of Line Charts
- Data Point Connection:The closing prices for each day or specific time period are connected with lines, forming a smooth curve.
- Key Focus:Line charts eliminate the distractions of opening price, highest price, and lowest price, allowing investors to concentrate on the overall price trend.
Applicable Scenarios
Line charts are simple and intuitive, making them especially suitable for analyzing long-term trends, such as weekly, monthly, or longer-term forex movements. These charts help investors quickly grasp the overall market direction and provide foundational support for developing trading strategies.
Example:
If you observe a consistent upward trend in the GBP/JPY line chart, it indicates increasing demand for the British pound. In this scenario, beginner investors may choose to follow the prevailing bullish trend in the short term while using stop-loss levels to manage risk.
From Simplicity to Complexity: Choosing the Right Forex Trading Tools
In forex trading, different charting tools provide varying levels of information:
- Line chartsare ideal for beginners who want to focus on overall trends and quickly build market awareness.
- Bar chartsoffer more detailed price fluctuations for advanced traders, aiding in more precise decision-making.
- Candlestick charts,when combined with these tools, allow for a more comprehensive interpretation of market data and provide strong support for trading strategies.
As traders gain experience and apply these tools more flexibly, forex trading can become more structured and efficient.
Fundamental & Technical Analysis: A Perfectly Balanced Trading Strategy
Successful forex traders often integrate fundamental analysis and technical analysis to construct a complete trading strategy.
Example:
- Fundamental Analysisprovides a broader market outlook. For instance, if the S. Federal Reserve (Fed) raises interest rates, the U.S. dollar may strengthen, making it favorable for medium-to-long-term bullish trades on the USD.
- Technical Analysishelps identify optimal entry and exit points in the short term. When the U.S. dollar index rises, traders can use technical indicators—such as support and resistance levels—to find the best buying or selling opportunities.
Forex Trading Strategy Tutorial: Practical Methods and Techniques
After gaining a deep understanding of the basic operations and market dynamics of forex trading, formulating an appropriate investment strategy is key to achieving stable returns. This section will provide efficient and practical forex trading strategies tailored to different types of investors, helping you navigate market challenges flexibly and enhance your overall trading capabilities.
-
Mastering Core Factors Influencing Forex Prices
Forex market price fluctuations are typically driven by multiple external factors, including political events, economic data, and global market trends. To more accurately predict market movements, investors need to:
- Stay updated on international news: For example, leadership changes in a country, trade negotiations between major economies, or regional conflicts can significantly impact related currency pairs.
- Analyze economic indicators: Such as changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), U.S. Non-Farm Payroll reports, and monetary policy decisions by central banks.
- Example: If the Bank of Japan announces it will maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy while the Federal Reserve accelerates its rate hikes, this interest rate differential could lead to a rise in USD/JPY. Based on this news, you can seize short-term market volatility opportunities.
-
Choosing Suitable Currency Pairs: Based on Investment Style and Risk Appetite
Each currency pair has its unique volatility characteristics and trading activity levels, making the selection of appropriate currency pairs crucial for forex trading:
- Conservative investors: May prioritize highly liquid and relatively stable major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY.
- Aggressive investors: Can focus on more volatile minor currency pairs, such as GBP/NZD or AUD/CAD, to potentially achieve higher short-term returns.
- Tip: In-depth research on your chosen currency pairs, including their economic background and market characteristics, can effectively reduce unnecessary trading risks.
-
Start with Small Trades: Gradually Build a Trading Foundation
For forex trading beginners, controlling initial risks is crucial:
- Use small lot sizes: For example, opt for mini lots (0.1) or micro lots (0.01) to gradually familiarize yourself with market operations and price volatility patterns.
- Analyze trade records: Accumulate practical experience through small trades and review each trade to identify reasons for success or failure.
- Example: You can start with highly liquid currency pairs (e.g., EUR/USD) for day trading, gaining experience in judging market trends through short-term operations.
-
Adjust Strategies Flexibly Based on Market Conditions
The forex market is ever-changing, and fixed strategies may not adapt to market volatility. Therefore, flexibility is key to success:
- High-volatility markets: Suitable for short-term trading strategies like day trading or scalping to quickly capture price movements.
- Stable markets: Opt for medium- to long-term strategies, positioning based on overall market trends, such as holding long positions to capture upward trends.
- Example: Before the release of Non-Farm Payroll data, market volatility usually increases, making it a good time for short-term traders to use breakout strategies. During calm periods, trend-following medium-term strategies are more appropriate.
-
Control Leverage Ratios: Protect Capital with Robust Risk Management
Leverage in forex trading can amplify profits but also increase risks, so it must be used cautiously:
- Set reasonable leverage levels: Choose appropriate leverage based on your capital size, such as 1:30 or 1:50, to avoid over-leveraging.
- Implement strict stop-loss strategies: Ensure that the maximum loss per trade is within acceptable limits to prevent irreversible losses from excessive leverage.
-
Set Stop-Loss Points: Core Protection in Risk Management
Setting stop-loss points is a key measure to counter market unpredictability:
- Adjust stop-loss points based on market volatility: For instance, set wider stop-loss points during high-volatility periods and narrower ones during stable periods.
- Strictly execute stop-loss plans: Once the stop-loss point is reached, close the position decisively to prevent further losses from holding onto losing trades.
- Example: If you set a 50-pip stop-loss for a GBP/USD trade, execute the stop-loss immediately when the market price reaches that level to avoid potential larger losses.
How to Start Forex Trading: A Complete Guide to Help You Get Started
When you’re ready to step into the forex trading market, following the correct process is crucial. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced investor, mastering clear operational steps can help you start steadily in the forex market. Below are the three essential steps to get started with forex trading, from opening an account to analysis and actual trading, guiding you step-by-step toward success.
Step 1: Open a Forex Trading Account
The first step to start forex trading is to open a forex account. Through a forex trading account, you can conveniently buy and sell different currency pairs. Here are the basic requirements for opening an account:
Prepare Account Opening Documents:
You will need to provide:
- Identification documents (e.g., ID card, passport, driver’s license);
- A second document (e.g., health insurance card or bank passbook);
- Basic contact information, such as phone number and email address.
Account Opening Process:
- Choose an institution: You can opt for bank forex services or professional trading platforms. For example, some investors prefer using bank accounts for forex deposits, while others favor the flexibility of professional forex trading platforms.
- Submit documents and complete verification: After submitting the required documents, the bank or platform will review them to ensure eligibility.
- Fund your account: Once the account is approved, you can deposit funds and begin your forex trading journey.
- Tip: Choose a secure and reliable institution, such as a local bank or a regulated international forex platform, to ensure the safety of your funds.
Step 2: Learn Forex Market Analysis
After opening your account, the next step is to conduct market analysis. Forex market fluctuations are driven by various factors, and understanding market trends is key to making informed investment decisions.
How to Conduct Forex Analysis?
Forex market analysis mainly includes two aspects:
- Fundamental Analysis:
Focus on macroeconomic indicators that affect currency exchange rates, such as central bank policies, interest rate changes, unemployment rates, and GDP data.
For example, when a country’s central bank raises interest rates, it typically increases the attractiveness of that country’s currency, driving its exchange rate higher.
- Technical Analysis:
Use historical data and charts to analyze currency price trends and predict future movements.
Utilize technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, and candlestick charts to help you intuitively determine buy or sell opportunities.
For beginners, you can master these analysis techniques through professional books, online courses, or practical tools, gradually improving your trading skills.
Step 3: Start Forex Trading
Once you’ve grasped the basics of the forex market and analysis methods, you can start actual trading. At this stage, developing a clear trading strategy is particularly important.
How to Trade Effectively?
- Start with small lot sizes:
Beginners are advised to start with mini or micro lots to familiarize themselves with market dynamics using lower capital.
For example, if you want to trade EUR/USD, you can start with 0.01 lots, ensuring manageable risk even during market volatility.
- Choose major currency pairs:
Beginners can prioritize currency pairs with relatively low volatility, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY.
These pairs not only have high liquidity but also provide stable trading opportunities, helping to reduce trading risks.
- Set stop-loss and take-profit levels:
Stop-loss orders help limit potential losses, while take-profit orders ensure profits are locked in when targets are reached.
For example, if you buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, you can set a stop-loss at 1.0950 and a take-profit at 1.1050, allowing you to control risks in advance.
- Adapt to market changes:
The forex market is highly volatile, so it’s recommended to regularly review and adjust your trading strategies based on actual conditions.
During major economic data releases or global political events, you may need to act quickly.
Forex Trading: Recommended Margin CFD Platforms
Compared to other forex trading channels, forex margin Contract for Difference (CFD) trading offers unique advantages: low capital requirements, flexible two-way trading, and the ability to seize opportunities whether the market rises or falls. Additionally, the account opening process is convenient, with most platforms supporting online completion, allowing investors to start trading quickly. These advantages make forex margin trading an ideal choice for many investors to enhance capital efficiency.
Choosing a regulated and reliable forex margin CFD trading platform is a crucial step to ensure fund safety and fair trading. High-quality platforms provide transparent trading environments, professional trading tools, and diverse trading options, offering investors an excellent trading experience.
Choosing a Regulated Forex Trading Platform
Below are globally renowned forex trading regulatory authorities that provide legal protection and fund safety for investors:
- UK Financial Conduct Authority (FCA): One of the most authoritative financial regulators globally, known for its high regulatory standards.
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC): Strictly regulates broker behavior to ensure fair and transparent market operations.
- S. National Futures Association (NFA): Monitors brokers comprehensively to protect investor rights.
- European Union Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID): Provides unified trading regulations across the EU.
- Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC): Supported by the EU regulatory framework, ensuring good market compliance.
Choosing a platform certified by the above regulatory bodies can effectively reduce investment risks, ensure fund transparency, and provide a secure trading process. This is especially important for forex trading beginners, marking the first step toward stable investment.
Recommended Forex Trading Platforms
Some widely recognized forex trading platforms include **Ultima Markets**, **Vantage**, and **IC Markets**, all regulated by one or more of the above authorities.
Since I personally use Ultima Markets for trading and am more familiar with it, I recommend it here.
Ultima Markets is a trading platform under the Australian real estate developer Viapac Group (Pan Pacific Group), regulated by CySEC, ASIC, and the Mauritius Financial Services Commission (FSC). The platform offers over 60 forex currency pairs, as well as gold, silver, U.S. stocks, stock indices, and cryptocurrencies. Additionally, Ultima Markets provides zero commission, low spreads, leverage options from 1:1 to 1:2000, and minimum trade sizes as low as 0.01 lots. The platform also includes various trading tools, such as stop-loss, take-profit, trailing stop-loss, and real-time trading signals.

If you are not yet ready to trade with real funds, demo trading is an excellent option. Ultima Markets offers a free demo account that simulates real market conditions, allowing you to:
- Familiarize yourself with the operation of the forex trading platform without requiring funds or taking actual risks;
- Test your trading strategies and make adjustments as needed;
- Build confidence in a secure environment to prepare for live trading.
Through demo trading, you can grasp market patterns and improve your sensitivity to market fluctuations, laying a solid foundation for future real trading.
FAQ
Q: Is forex trading high risk?
A:
Forex trading carries a high level of risk due to the significant volatility of the forex market, which is influenced by multiple factors such as political events, economic data, and central bank policies. Additionally, forex trading utilizes leverage, which amplifies both potential returns and risks. While leverage can accelerate capital growth, it can also lead to rapid losses.
For beginner traders, learning effective risk management is crucial. Setting stop-loss points, controlling leverage ratios, staying calm, and avoiding overtrading are essential strategies to mitigate risks. In summary, while the forex market offers profit opportunities, the high risk involved requires investors to act with caution.
Recommendation: If you are new to forex trading, start with small trades and choose a regulated platform to minimize risk and build confidence.
Q: How much forex trading profit is taxable?
A:
In Taiwan, profits from forex trading are subject to taxation. Whether short-term or long-term trading, any profits earned must be reported in accordance with regulations. Specifically:
- Tax classification:Forex trading profits are usually categorized as “property transaction income.” If trading is frequent, it may be classified as regular income and taxed under income tax regulations.
- Tax reporting threshold:If annual profits exceed TWD 160,000, you must file and pay taxes accordingly.
- Tax filing process:Taxpayers must submit their annual comprehensive income tax return in May and provide transaction records to calculate gains and losses.
- Record-keeping:Keeping detailed transaction records is essential for accurate tax reporting.
In short, any profits must be reported for taxation. To avoid complications, it is recommended to maintain comprehensive transaction records and consult a tax professional.
Q: How to determine forex rate trends?
A:
Determining forex rate trends requires a comprehensive analysis of multiple factors.
- Fundamental analysis:Investors should monitor key economic indicators such as GDP, unemployment rates, and inflation rates, as these reflect a country’s economic health and influence its currency value. Additionally, central bank interest rate decisions play a crucial role—rate hikes typically strengthen a currency, while rate cuts may lead to depreciation. Political events, such as elections, policy changes, and trade agreements, can also trigger forex fluctuations.
- Technical analysis:Traders use candlestick charts, trend lines, support and resistance levels to predict market trends. Moving average crossovers, especially between short-term and long-term moving averages, often signal trend shifts.
- Market sentiment and investor behavior:The market’s risk appetite (such as confidence in economic growth or fear of uncertainty) affects capital flow and forex price movements.
By integrating these factors, traders can enhance their ability to assess forex rate trends more accurately.
Q: What happens in a forced liquidation?
A:
Forced liquidation occurs when a forex trading account lacks sufficient funds to maintain the required margin, prompting the broker to automatically close positions to prevent further losses.
This typically happens during extreme market volatility or when the trader fails to deposit additional margin in time. Forced liquidation means traders lose control over their closing prices, which can result in greater losses, especially if the market continues to move unfavorably after liquidation.
To avoid forced liquidation, it is essential to:
- Maintain adequate margin levels;
- Set stop-loss orders;
- Monitor market conditions regularly.
Failure to do so could lead to complete depletion of account funds.
Q: How to receive international wire transfers?
A:
Receiving international wire transfers typically involves the following steps:
- Provide banking details:Share your bank account information, including the International Bank Account Number (IBAN), SWIFT code (or BIC code), bank name, and bank address. These details ensure accurate fund transfers.
- Choose a transfer method:Common international transfer methods include wire transfers, PayPal, and Western Union, each with different processing times and fees.
- Inform the sender about applicable fees:International transfers may incur transaction fees, which can be borne by either the sender or receiver, depending on the agreement.
- Confirm receipt of funds:Depending on the transfer method, funds typically arrive in your account within a few business days. You can verify the transaction through online banking or by contacting your bank.
Before making international transfers, understanding exchange rates, transaction fees, and possible conversion charges is crucial to ensure smooth transactions.






![[MetaTrader 5 Mobile Trading Complete Guide] 7 Key Advantages for Real-Time Market Access](https://www.ultimamarkets.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/mt5_mobile_trading_card.jpg)