Understanding Canada’s Inflation Control and the BOC’s Monetary Policy
Within the intricate realm of economics, grasping the nuances of inflation control stands as a paramount endeavor. This article embarks on an exploration of Canada’s adept strategies for effectively managing inflation, while shedding light on the rationale behind the Bank of Canada’s (BOC) choice to uphold a 5% interest rate during its pivotal October 2023 meeting.
BOC Keeps Policy Rates Steady at 5%
During its October meeting, the BOC chose to maintain the overnight rate at 5%. This decision has far-reaching implications, and to understand them, we need to explore the BOC’s broader monetary strategy.
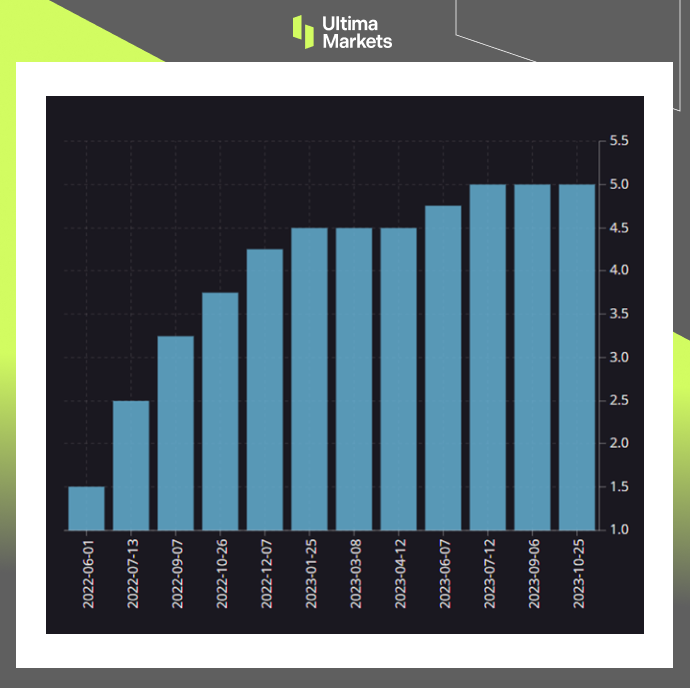
(Policy interest rate, BOC)
The Path to Stability: BOC’s Quantitative Tightening Policies
Quantitative tightening policies are at the forefront of the BOC’s monetary strategy. These policies encompass a series of actions aimed at tightening the money supply and controlling inflation. They are pivotal in ensuring economic stability and facilitating future growth.
What Are Quantitative Tightening Policies?
Quantitative tightening policies involve reducing the money supply by selling government bonds or other assets. By doing so, the BOC can absorb excess liquidity in the market, which, in turn, puts upward pressure on interest rates.
Understanding Canada’s Inflation Control
A pivotal metric under the constant scrutiny of the BOC is the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI serves as a barometer of inflation, capturing the evolving costs of a diversified basket of goods and services over time. In recent months, Canada’s CPI has demonstrated a degree of volatility, warranting close attention.
Canada Inflation Levels Getting Under Control
- In June, the CPI was at 2.8%.
- August saw a sharp increase, with the CPI reaching 4.0%.
- September reported a CPI of 3.8%.
Bank Of Canada’s Projections
The BOC’s latest projections provide valuable insights into the future of inflation in Canada:-
Short-Term Outlook
- The BOC’s projections suggest that the CPI is poised to maintain an average of approximately 3.5% until the middle of the upcoming year.
- Short-term inflation trends are primarily steered by the influence of energy prices and the enduring presence of core inflation factors.
Long-Term Goals
- Post-mid next year, the BOC projects a gradual decrease in inflation.
- The ultimate goal is to reach a 2% inflation rate by 2025, signifying a more stable economic environment.
Conclusion
Canada’s economic panorama is intricately intertwined with the monetary policy choices of the BOC and its strategies for inflation management.
Vigilantly monitoring these evolutions empowers individuals and enterprises to make judicious financial decisions, adeptly traverse the economic terrain, and play a role in upholding the nation’s economic equilibrium.
Grasping the BOC’s position on interest rates and inflation control is of paramount importance for anyone with a stake in the Canadian economy, ensuring they remain well-informed and well-prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie on the horizon.








